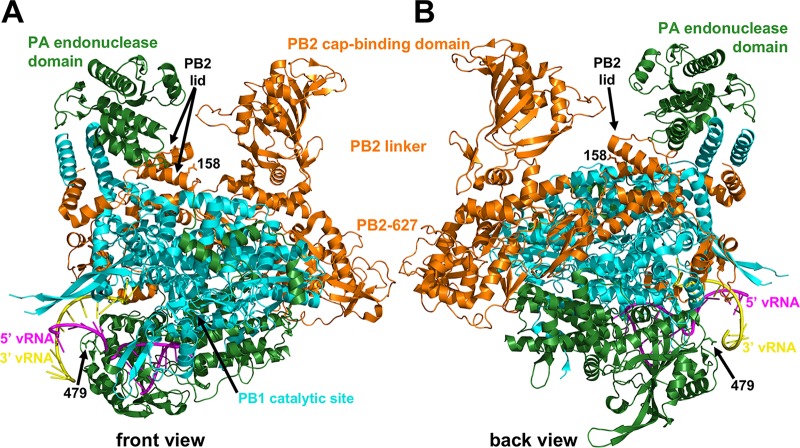
FIG 9.
Polymerase structure and locations of mouse-adaptive mutations. Shown are front (A) and back (B) views of the polymerase complex from A/little yellow-shouldered bat/Guatemala/060/2010 (H17N10) (PDB accession no. 4WSB) (41). The proteins are identified by maintaining the original color conventions for PA (green), PB2 (orange), and PB1 (cyan). The PA endonuclease, PB2 cap-binding, PB2 linker, PB2-627, PB2 lid, and PB1 catalytic-site domains are labeled. Residues PA-D479 (479) and PB2-E158 (158) are the only residues for which sidechains are shown. 5′ (magenta) and 3′ (yellow) viral RNAs are also shown. PA-D479 is positioned at the bottom of a rim that funnels up into the polymerase channel. PB2-E158 is located in an α-helical lid that directs newly captured caps down into the PB1 catalytic site and prevents newly synthesized RNA from being cleaved by the PA endonuclease domain when it exits the top of the polymerase.