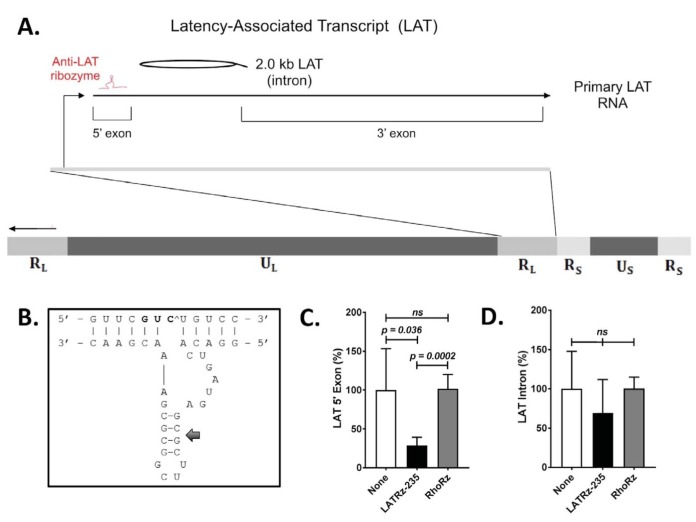
FIG 1.
Schematic of the HSV-1 genome showing the regions encoding the HSV-1 LAT and design and in vitro testing results of a ribozyme targeting the LAT. (A) The LAT locus (located in both copies of the RL region of the genome) is expanded to show the 8.5-kb primary LAT, the 5′ and 3′ exons, and the stable 2.0-kb intron. (B) Design of a synthetic hammerhead ribozyme targeting the LAT 5′ exon. The 5′ exon of the HSV-1 LAT was analyzed for hammerhead cleavage sequences. Antisense flanking regions were designed around the conserved catalytic domain to hybridize with the region surrounding the selected triplet. Mfold analysis predicted base pairing in stem II (arrow), but not in the flanking regions, so as to rule out intramolecular base pairing interfering with efficient binding between the ribozyme and the target. (C and D) Quantification of the HSV-1 LAT 5′ exon (C) and the 2.0-kb LAT intron (D) in rabbit skin cells following transfection with a LAT-expressing plasmid and either mock treated or cotransfected with LATRz-235 or RhoRz. RNA was isolated, cDNA was transcribed, and LAT levels were analyzed by TaqMan real-time PCR that was normalized to the untargeted cellular control rabbit GAPDH. Normalized data are graphed as percentages of the 5′ exon or LAT intron in treated cells relative to untreated cells (None). Each bar represents the average expression of four wells of a 24-well plate (n = 4). Error bars represent standard deviations.