Figure 2.
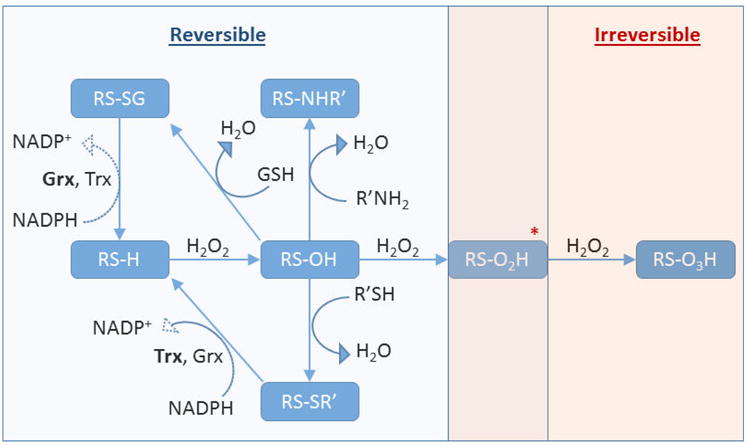
Cysteine Posttranslational Modifications. Protein thiols (RS-H) can undergo oxidation to the sulfenic acid (RS-OH), which then can react with intracellular glutathione to form a mixed disulfide (RS-SG) or with another protein moiety such as another thiol to form a disulfide bond (RS-SR') or an amine to form a sulfenamide (RS-NHR'). These modifications are reversible and can be reduced back to the thiol, enzymatically, at the expense of NADPH. The sulfenic acid can be further oxidized to the irreversible modifications sulfinic acid (RS-O2H) and sulfonic acid (RS-O3H)*. It has been demonstrated that the hyperoxidized sulfinic acid in the peroxiredoxin can be enzymatically reduced to the sulfenic acid at the expense of ATP, and as such it is possible that other unidentified proteins may utilize a reversible sulfinic acid in their function.
