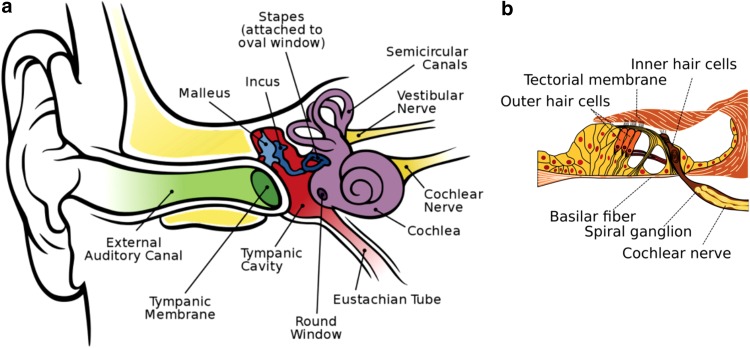
FIG. 1.
Anatomy of the human ear. (a) The outer ear includes the ear lobe and auditory canal; middle ear, the tympanic membrane and cavity; the inner ear, the hearing (cochlea) and balance (vestibular system) organs and the attached associated nerves connecting to the brain. (Figure reproduced from Chittka L, Brockmann A. Perception space—the final frontier. PLoS Biol. 2005;3(4):e137. CC BY 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5/deed.en), via Wikimedia Commons. Original File URL: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_of_the_Human_Ear_en.svg) (b) Expanded cross section of the cochlea (organ of Corti) showing the outer and inner hair cells, and the spiral ganglion of the cochlear nerve. (Cochlea-crosssection.png. CC BY-SA 3.0 US (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/us/), via Wikimedia Commons. Original File URL: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Organ_of_corti.svg)