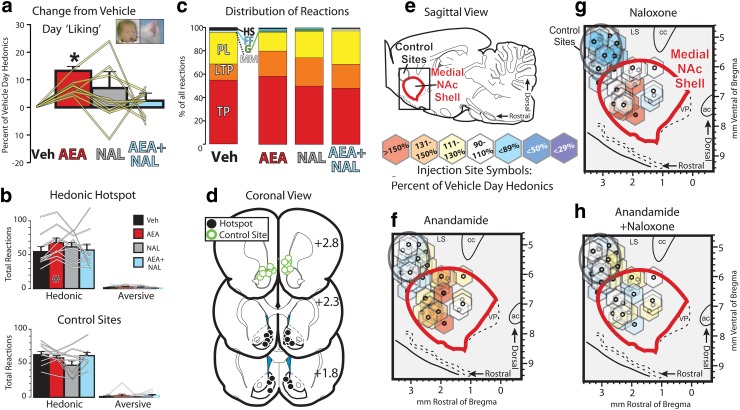
FIG. 1.
Anandamide-induced hedonics require endogenous opioid signaling in NAc shell hedonic hotspot. (a) Percent increase in hedonic reactions to sucrose from vehicle day behavior is shown. Bars indicate group mean and standard errors. Yellow lines represent values for each tested rat with cannulae placed within the medial NAc shell hedonic hotspot. Veh, vehicle; AEA, anandamide, NAL, naloxone; AEA+NAL, cocktail injection of anandamide and naloxone. (b) Total hedonic (left) and aversive (right) reactions to sucrose are shown for rats with cannulae in NAc (top) or at rostral control sites (bottom). Group mean/SEMs are represented with bars, and individual rat data are shown with gray lines. (c) Distribution of individual scored reactions are shown for each drug condition, with height of each bar representing the mean percentage of all reactions emitted for each drug. Hedonic Reactions: TP, tongue protrusion; LTP, lateral tongue protrusions; PL, paw lick; Neutral Reaction: MM, mouth movement; Aversive Reactions: G, Gape, FF, forelimb flails; HS, head shake. (d) Coronal view of cannulae localizations. Cannulae sites of control rats are shown in green, and rats with cannulae in the NAc are shown in black. (e) Diagram in sagittal view of the NAc Shell and control sites tested in this study. Hexagons at bottom define the color coding of (f–h), with each color representing the behavioral effect of a drug treatment, relative to that of animals' vehicle day hedonic reactivity. (f) Anandamide effects on hedonic reactivity are shown for each rat (placements are represented by hexagons, with size based on putative spread of microinjected drugs in the testing period21). Red, orange, and yellow colors represent increases from vehicle day after (f) anandamide, (g) naloxone, or (h) anandamide+naloxone in individual rats. NAc, nucleus accumbens; SEM, standard error of the mean.