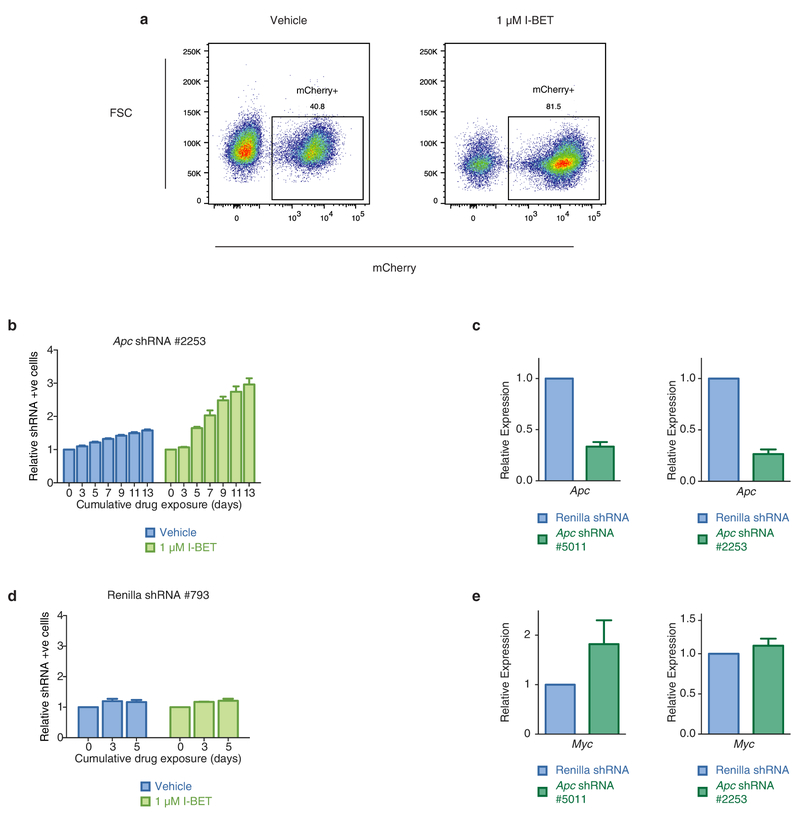
Extended Data Figure 9 |. shRNA-mediated knockdown of Apc confers resistance to sensitive clones.
a, shRNA-mediated knockdown of Apc, a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signalling, confers resistance to vehicle-treated clones. BET inhibitor treatment enriches for shRNA-containing (mCherry-positive) cells. Representative FACS plots after 7 days of cumulative drug exposure to either vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or 1 μM I-BET in a vehicle clone transduced with an Apc shRNA. b, c, Independent shRNAs directed against Apc confer resistance to vehicle-treated clones. Viable, shRNA-positive cells after treatment with either vehicle or I-BET normalized to day 0 performed in biological triplicate (mean ± s.d.). qRT–PCR data from FACS-isolated shRNA-containing cells performed in biological duplicate (mean ± s.e.m.). d, I-BET treatment of vehicle-treated clones transduced with a non-targeting shRNA does not enrich for shRNA-containing cells. Viable, shRNA-positive cells after treatment with either vehicle or I-BET normalized to day 0 performed in biological triplicate (mean ± s.e.m.). e, shRNA-mediated knockdown of Apc results in increased expression of Wnt/β-catenin target gene Myc. qRT–PCR data from FACS isolated shRNA containing cells performed in biological duplicate (mean ± s.e.m.).