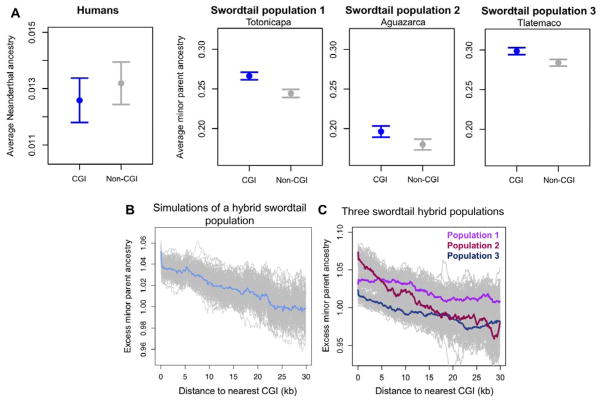
Figure 4. The recombination mechanism shapes the distribution of minor parent ancestry.
(A) Neanderthal ancestry is not elevated in 50 kb windows that overlap with CpG islands (CGIs), when compared to windows that do not, but have similar GC content. The fold difference λ is 0.95 (p=0.91; see 21). The same analysis in swordtail hybrids reveals that minor parent ancestry is higher in windows that overlap CGIs (pop. 1, λ=1.09, p<0.005; pop. 2, λ=1.09, p<0.005; pop. 3, λ=1.02, p<0.005). Points show the mean and whiskers indicate two standard errors of the mean obtained by 1,000 joint bootstraps. (B) Simulations of incompatibility selection in swordtails predict higher minor parent ancestry near CGIs. (C) This prediction is met for all hybrid populations. In B and C, gray lines show results of 500 replicate simulations bootstrapping 5 kb windows; colored lines indicate the mean of all replicates in sliding 5 kb windows.