Extended Data Figure 3. Inhibition of GPe-PV neuron activity modestly affects cocaine-induced locomotion.
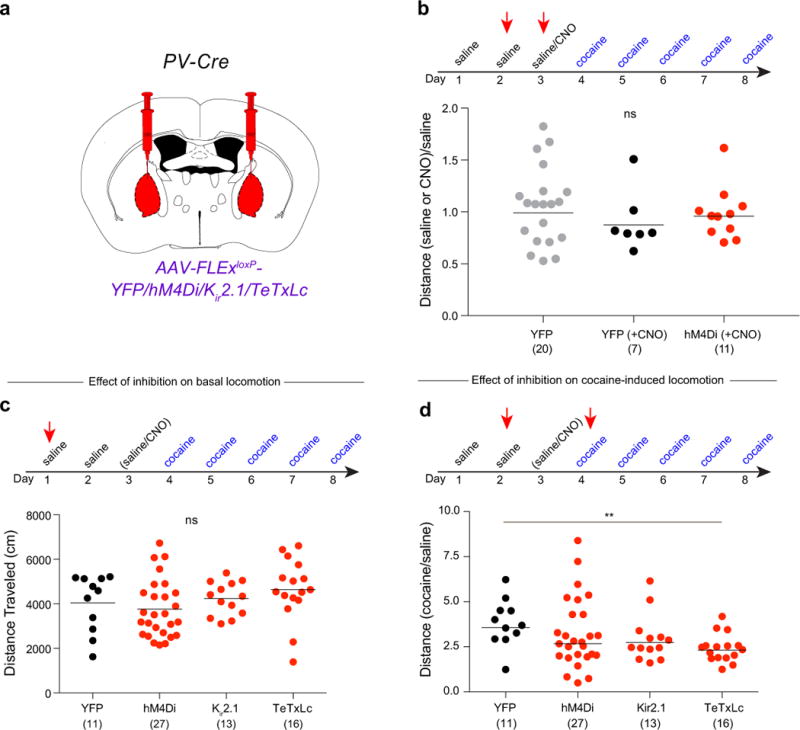
a, Cre-dependent AAVs expressing YFP, hM4Di, Kir2.1, or TeTxLc were injected into the GPe of PV-Cre animals. b, Quantification of effects of CNO on basal locomotion in animals expressing YFP or hM4Di (compared to YFP + saline: YFP + CNO, p = 0.36; hM4Di + CNO, p = 0.59). c, Quantification of basal locomotion during GPe-PV neuron inhibition (hM4Di, p = 0.54; Kir2.1, p = 0.66; TeTxLc, p = 0.27). d, Quantification of cocaine-induced locomotion during GPe-PV neuron inhibition (hM4Di, p = 0.37; Kir2.1, p = 0.12; TeTxLc, p = 0.002). The schematics of the mouse brain in this figure were adapted from ref. 33.
