Figure 5.
Deletion of Mettl3 or Fto in Adult Excitatory Neurons of the Hippocampus CA1 and CA3 via a Nex-CreERT2 Driver Line and Knockout Induction in Adult Animals via Tamoxifen Administration Alters Gene Expression in Animals
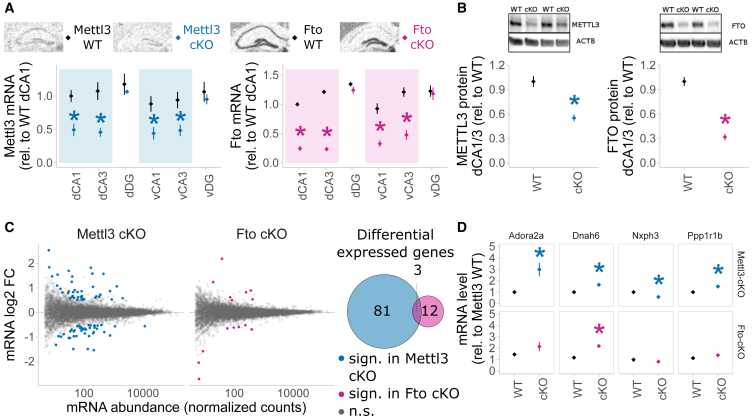
(A) Mettl3 and Fto mRNA are depleted from the dorsal (d) and ventral (v) hippocampus CA1 and CA3 in Mettl3 cKO (blue) and Fto cKO (pink) mice, respectively. WT, wild-type; cKO, conditional knockout; DG, dentate gyrus. In situ hybridization; expression was quantified from digitalized films in arbitrary units (AU); mean ± SEM, n = 4 for Mettl3 WT and cKO, n = 11–14 for Fto WT and cKO, signal averaged across both hemispheres; ∗p < 0.05, t test.
(B) METTL3 and FTO proteins are significantly depleted in Mettl3 cKO and Fto cKO mice, respectively. Protein was isolated from dissected dCA1/dCA3 and measured by western blot normalized to ACTB protein. n = 3–4, optical density normalized from digitally acquired images, mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, t test. For full blots, see Figure S6.
(C) mRNA-seq of adult CA1 and CA3 shows altered gene expression after deletion of Mettl3 and Fto in non-stressed basal animals. More genes are differentially expressed after deletion of Mettl3 (84) compared to deletion of Fto (15), with very few overlapping (3). log2 change by DESeq2 baseMean gene abundance from RNA-seq of adult basal animals. Differentially expressed by colored dots and in Venn circles, Q < 0.1, log2 fold change > 0.5.
(D) Four representative examples of genes expressed in a knockout × genotype-specific pattern. In total, 104 genes were found to be expressed in a knockout × genotype interaction-dependent matter. Normalized counts relative to Mettl3 WT. n = 5.
See also Figures S6 and S7 and Table S4.