Figure 6.
Animals with Adult Excitatory Neuron-Specific Depletion of Mettl3 and Fto Using a Nex-CreERT2 Driver Line Have Impaired Fear Coping, Differential Transcriptomic Response to Fear, and Changes in Hippocampus CA1 Electrophysiological Properties
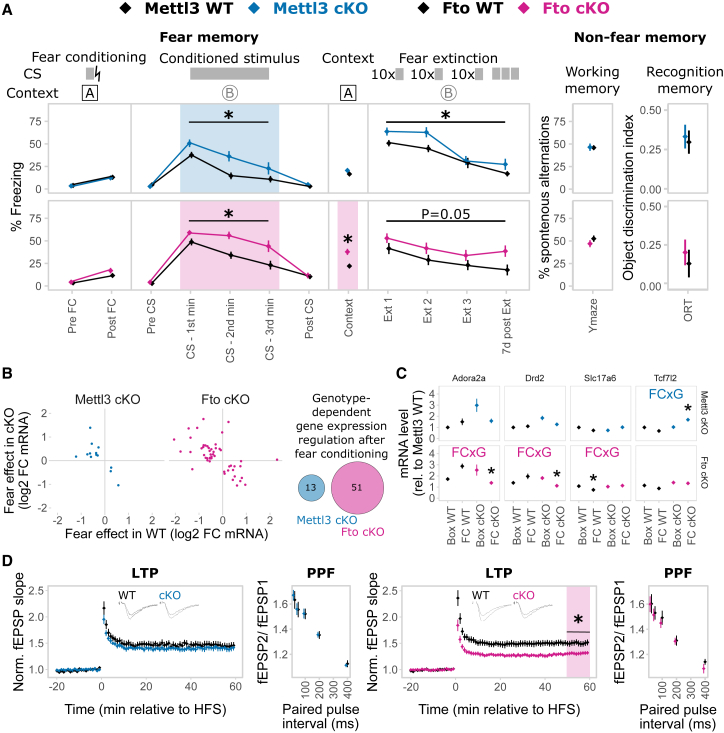
(A) Both Mettl3 cKO and Fto cKO animals display increased conditioned fear memory long-term maintained during fear extinction. The primary fear response was not altered. Fto cKO animals also have increased contextual fear memory. No difference was observed in the Y-maze test or the object recognition test (ORT). CS, conditioned stimulus; lightning bolt, US, unconditioned stimulus; Ext, extinction. n = 11–13, mean ± SEM. Fear expression was binned in 1 min intervals during CS representation. Asterisk (∗) depicts a main genotype effect in repeated-measurements ANOVA for CS and Ext bins and a t test p < 0.05 for all other data points.
(B) The transcriptomic response 24 hr after fear conditioning (FC) is altered in both animals with Mettl3 or Fto depletion. log2 RNA fold change in WT versus cKO animals of only those genes with a significant genotype × FC effect. Q < 0.1, absolute log2 fold change > 0.5, n = 5.
(C) More genes express a genotype-dependent FC effect in Fto cKOs compared to Mettl3 cKOs with low overlap. Four examples of such genes are shown. Significant genotype × FC in the examples is depicted by blue (Mettl3 cKOs) and pink (Fto cKOs) opposite arrows. Q < 0.1, absolute log2 fold change > 0.5, n = 5.
(D) Long-term potentiation (LTP), but not short-term plasticity, in CA1 was attenuated in Fto cKO mice, but not Mettl3 cKO mice. Short-term synaptic plasticity was measured by paired-pulse facilitation (PPF). n = 10–12 slices from 5–6 animals, mean ± SEM plus representative LTP trace curves; HFS, high-frequency stimulation. ∗p < 0.05, t test, on the average field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) slope 50–60 min post-HFS.
See also Figures S6 and S7 and Table S4.