Figure 4.
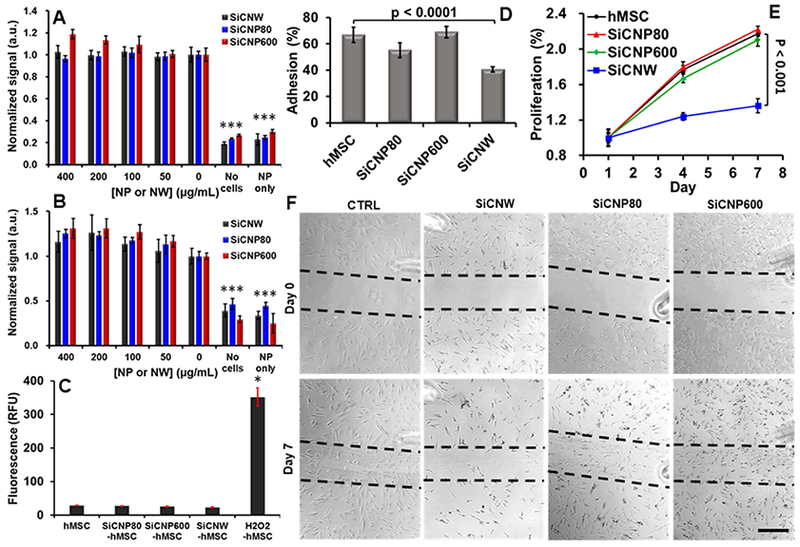
Influence of SiC on hMSCs’ viability, oxidative stress, adhesion, proliferation, and migration ability. (A) The MTS assay showed no significant decrease in cellular metabolism at any combinations of materials and concentrations (up to 400 μg/mL) (p > 0.05). (B) A calcein AM cell viability assay shows no significant decrease in viability at any concentration from 0–400 ug/mL (p > 0.05). (C) SiC labeling did not generate intracellular reactive oxygen species. (D) SiCNWs decreased the adhesion ability of hMSCs by more than 50%. (E) SiCNWs greatly decreased proliferation of hMSCs. (F) A migration assay shows hMSCs can migrate after labeling with SiCNWs and SiCNPs. However, there are fewer cells in the scratched area on the seventh day in hMSCs labeled with SiCNWs compared to the hMSCs labeled with SiC nanoparticles. Scale bar is 500 μm. Dashed black lines were added as guides. *** represents p < 0.005 compared to hMSC groups, unpaired Student’s t-test. Error bars represent standard deviations at least four replicates.
