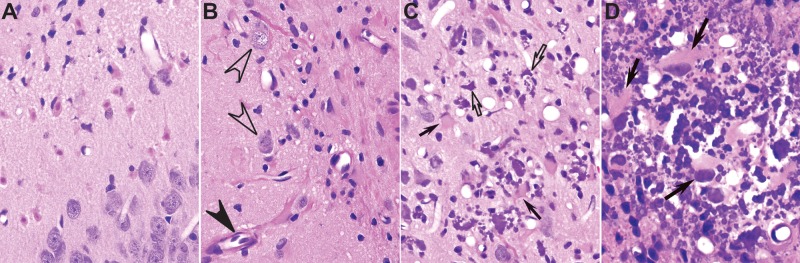
FIG. 2.
Types of lesions observed in the brain of rats acutely intoxicated with diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP). A–D, Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin-eosin–stained brain sections from the same animal at 28 days post exposure (DPE). A, Neuronal necrosis in the amygdala. B, Reactive astrogliosis in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, characterized by hypertrophic astrocytes with long fibrillary hypereosinophilic processes surrounding blood vessels (closed arrowhead). Note that healthy neurons (open arrowheads) are still present in areas of neuronal cell loss and glial scarring. C, D, Mineralization (open arrows) in the thalamus, associated with acute neuronal necrosis and hypertrophic activated astrocytes, characterized by a large cytoplasm, short thick processes and a peripheralized nucleus (closed arrows). Magnification: ×400 (A–C); ×600 (D).