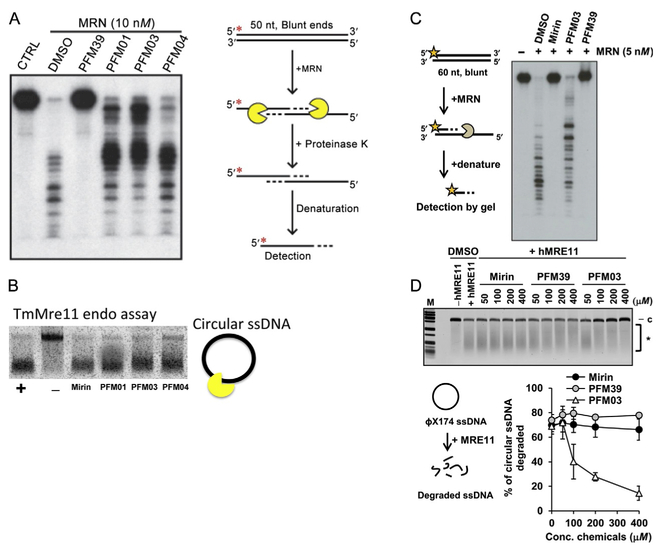
Fig. 7.
Nuclease activities and inhibitor impact. (A) MRE11 inhibitor PFM39 blocks MRN exonuclease activity (10 nM). In contrast, the MRE11 endonuclease inhibitors (PFM01, PFM03, and PFM04) have little effect on the MRN exonuclease activity. Radiolabeled DNA (100 nM) was incubated with MRN at 37°C for 60 min. Reactions contained a final concentration of 0.5 mM of the inhibitors. Red asterisk represents the 5′ radioactive label on the DNA. (B) Endo inhibitors PFM01, PFM03, and PFM04 primarily reduce the endo activity of TmMre11 vs the exo inhibitor Mirin. The nuclease assay is done at constant temperature and stopped at specific times. (C, D) The strong exo inhibition effect of PFM39 and Mirin vs endo inhibitor PFM03 for human MRN. (D) The strong endo inhibition activity of PFM03 vs the exo inhibitor mirin and PFM39 to human MRE11. The figure shows the percentage of circular ssDNA degraded relative to the control. Panels (C) and (D): Reproduced from Shibata, A., Moiani, D., Arvai, A. S., Perry, J., Harding, S. M., Genois, M. M., et al. (2014). DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice is directed by distinct MRE11 nuclease activities. Molecular Cell, 53(1), 7–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.11.003.