Fig. 8.
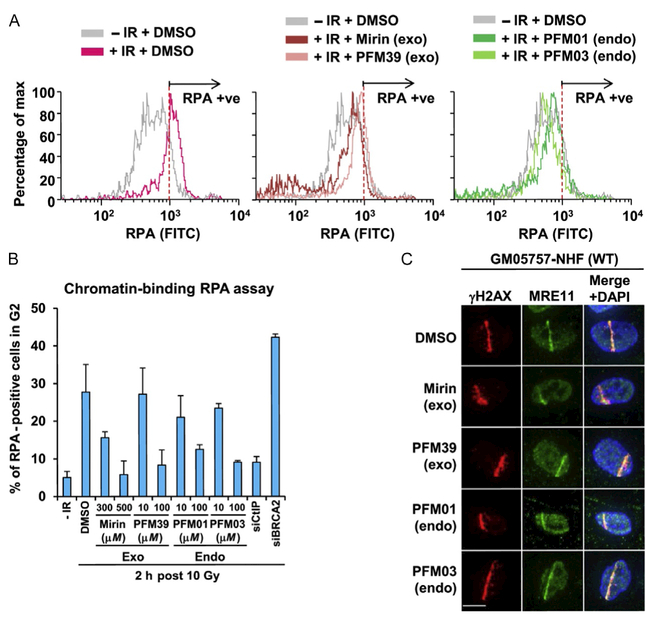
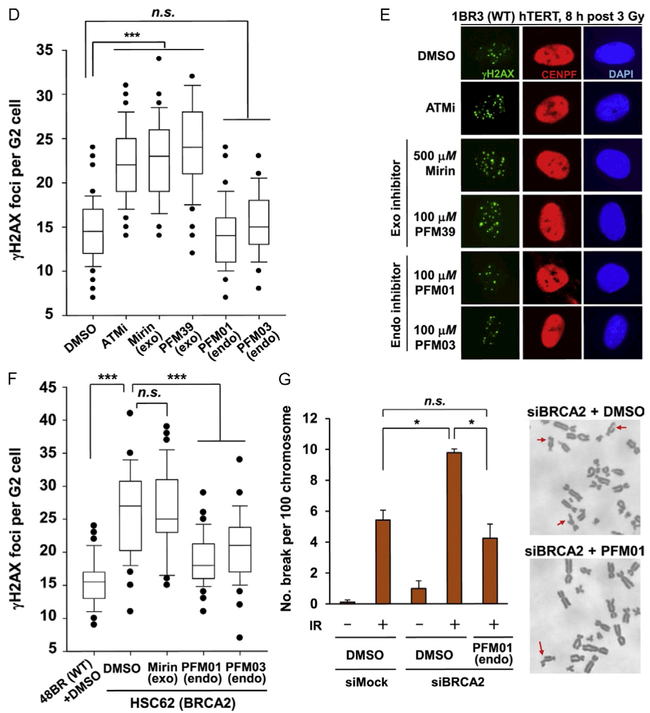
In cell validation assays from our publication (Shibata et al., 2014). (A) The effect that MRE11 inhibitors have in reducing chromatin-bound RPA level after IR treatment. IR-induced RPA retention in A549 cells was monitored by FACS analysis at 2 h post 10 Gy IR. (B) The quantification of RPA–FACS analysis at two different inhibitor concentrations. (C) Treatment with inhibitor does not affect the recruitment of MRE11 to the site of DNA damage. The cell lines used are primary human fibroblasts GM05757 subjected to UV-microbeam. The analysis of recruitment was done 1 h after inhibitor treatment. To identify the damage site, the histone γH2AX was labeled. (D, E) Treatment with exo inhibitor (but not endo inhibitors) causes a DSB repair defect in G2. DSB repair in G2 (CENPF+) cells was investigated by γH2AX foci analysis. Inhibitors were added 30 min before ionizing radiation (IR) treatment. 1BR3(WT) hTERT was fixed and stained at 8 h posttreatment with 3 Gy IR. (F) MRE11 endo inhibitors rescue the repair defect in HR-defective cells. γH2AX foci were enumerated in 48BR (WT) and HSC62 (BRCA2-defective) primary cells at 8 h posttreatment with 3 Gy IR. (G) The chromosome break defect in BRCA2 siRNA-treated 1BR3 (WT) hTERT was reversed by treatment with an MRE11 endonuclease inhibitor.