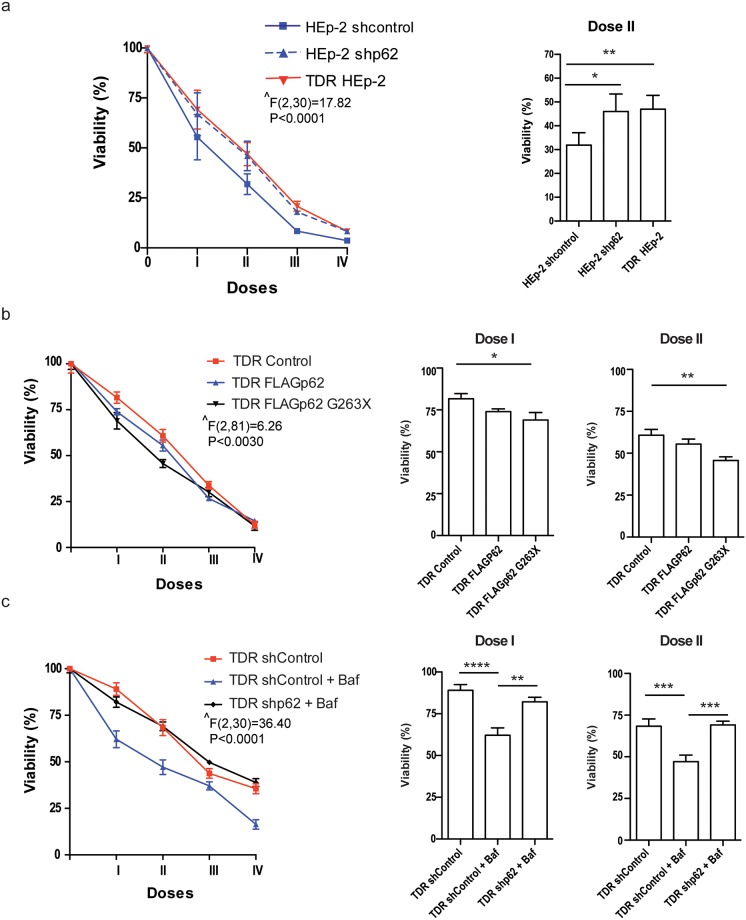
Fig 5. Role of p62 in chemoresistance in HEp-2 cells.
(a) Cell viability in response to combined treatment with increasing combined doses of cisplatin, 5-FU, and docetaxel for 24 h in stably p62-silenced parental HEp-2 as compared with mock-transduced HEp-2 (shcontrol) and TDR HEp-2 cells, by MTT assay. I-IV indicate the progressively doubling concentrations of cisplatin (μM), 5-FU (μM) and docetaxel (nM), respectively: I, 1, 20, 3; II, 2, 40, 6; III, 4, 80, 12; IV, 8, 160, 24. (b) Effect of combined treatment with increasing doses of cisplatin, 5-FU, and docetaxel on cell viability, as in (a), in TDR HEp-2 cells engineered to express a FLAG epitope-tagged full length p62 (FLAGp62) or a FLAG-tagged truncated mutant lacking both the ubiquitin- and LC3-binding domains (FLAGp62 G263X), as compared with control mock-transduced TDR HEp-2 cells (Control). The western blot analysis of full-length and truncated p62 expression in engineered TDR HEp-2 cells is shown in S6c Fig. (c) Assessment of combined drug toxicity as in (a) and (b) in TDR HEp-2 cells treated with bafylomycin-A1 (Baf) upon stable lentiviral p62 silencing (shp62) as compared to mock-transduced TDR HEp-2 cells (shControl). (a-c) Left: dose-response viability curves. Right: effect exerted by the indicated combination (mean ± SEM). Two-way ANOVA (group x treatment) with Bonferroni post-hoc test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001; n = 4 in (a), 6 in (b), 3 in (c). ^ main effect of group.