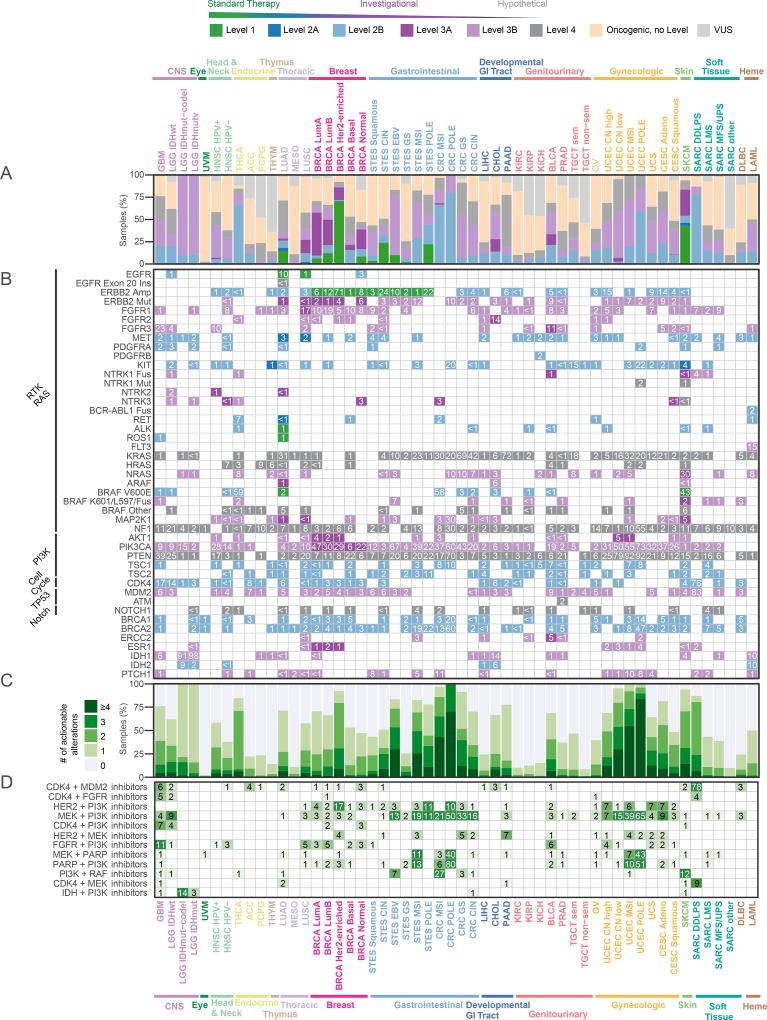
Figure 7. Therapeutic actionability and drug combinations.
(A) Frequencies of clinical actionability by cancer subtype, broken down by level of evidence (Levels 1–4). Samples are classified by the alteration that carries the highest level of evidence. Tumor type–specific samples are analyzed by variants considered actionable, oncogenic but not actionable, or variants of unknown significance (VUS). (B) Frequencies of actionable alterations per gene across cancer subtypes. For genes with different levels for different alterations, multiple rows are shown. Genes are grouped by pathway. Six additional genes not in the ten pathways (BRCA1, BRCA2, ERCC2, IDH1, IDH2, ESR1) are included and taken into account in the overall frequencies. (C) Fraction of samples with a given number of actionable alterations per tumor type. (D) Frequencies of possible drug combinations indicated by the co-alteration of actionable variants in each tumor type for the most frequent drug class combinations.