Figure 3. LPS treatment leads to a reduction in HCN1 and TRIP8b expression in CA1 pyramidal neurons.
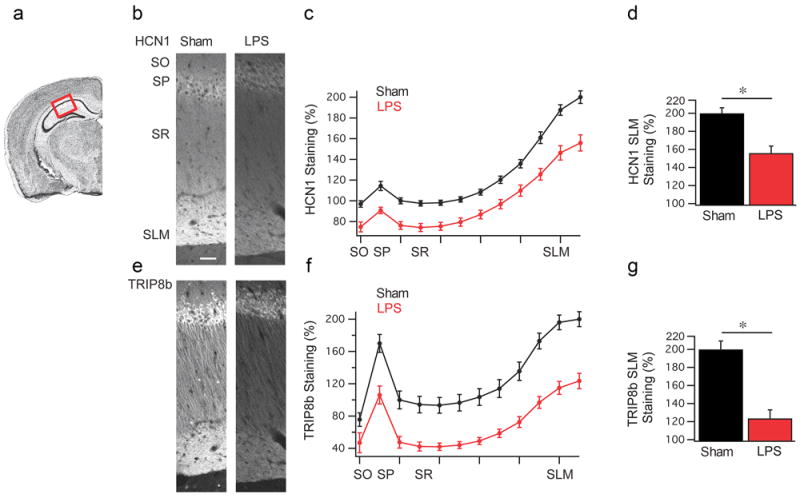
(a) Coronal view of the mouse hippocampus, highlighting the CA1 region used for quantification. (b) Representative HCN1 staining from rats 24 h after vehicle (n=6) (left) or LPS (n=6) (right) injection. SO: stratum oriens, SP: stratum pyramidale, SR: stratum radiatum, SLM: stratum lacunosum moleculare. (c) Quantification of the HCN1 staining shown in panel (b). (d) HCN1 staining in the SLM region was significantly reduced in LPS treated animals relative to vehicle controls (Sham). (e) Representative TRIP8b staining. (f) Quantification of TRIP8b staining. (g) TRIP8b staining was reduced in the SLM of LPS treated rats relative to controls (Sham). Data are mean±s.e.m. * p<0.05 by Mann–Whitney test. Scale bar: 50 μm.
