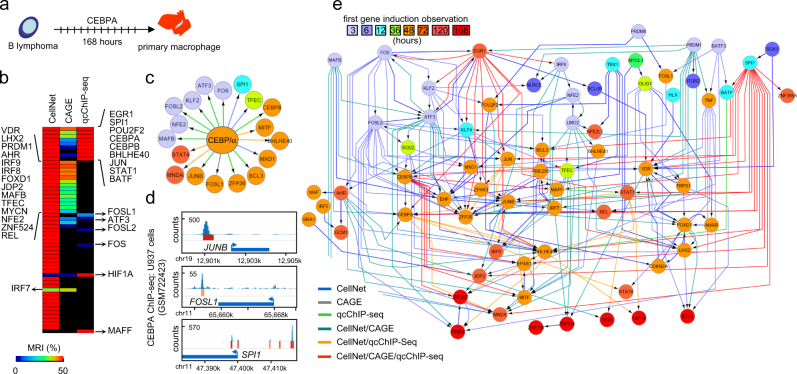
Fig. 2.
Reconstructing the TF regulatory network involved in B-lymphoma to macrophage trans-differentiation with TETRAMER. a TETRAMER was used to model the TF regulatory network implicated in trans-differentiation of B-lymphoma cells to primary macrophages by over-expression of CEBPA.19 b The information on temporal transcriptional regulation obtained from transcriptomes assessed during the first 168 h after CEBPA over-expression (GSE44700) was combined with the connectivity information obtained from three publicly available GRN sources [CellNet; regulatory circuits established by the FANTOM consortium (regulatorycircuits.org) and systematic reanalysis of all publicly available ChIP-seq datasets (ngs-qc.org)] to predict TFs that acted as master regulators of the trans-differentiation. Heat-maps of TFs identified by integrating each of the three GRN sources were ranked according to their MRI for comparison. c C/EBPα cistrome predicted from (b). d Verification of three predicted C/EBPα targets in (c) by ChIP-sequencing readouts available in the public domain (ngs-qc.org). Note that these three cases were predicted by the various publicly available GRN sources, as indicated by the arrow color-code (displayed in (e)). e The action of TFs (nodes are color-coded according to gene induction, as indicated at the top) in a GRN generated with TETRAMER, highlighting their temporal regulation during B-lymphoma to macrophage trans-differentiation. The origin of the integrated edges is color-coded to reveal the corresponding connectivity data sources