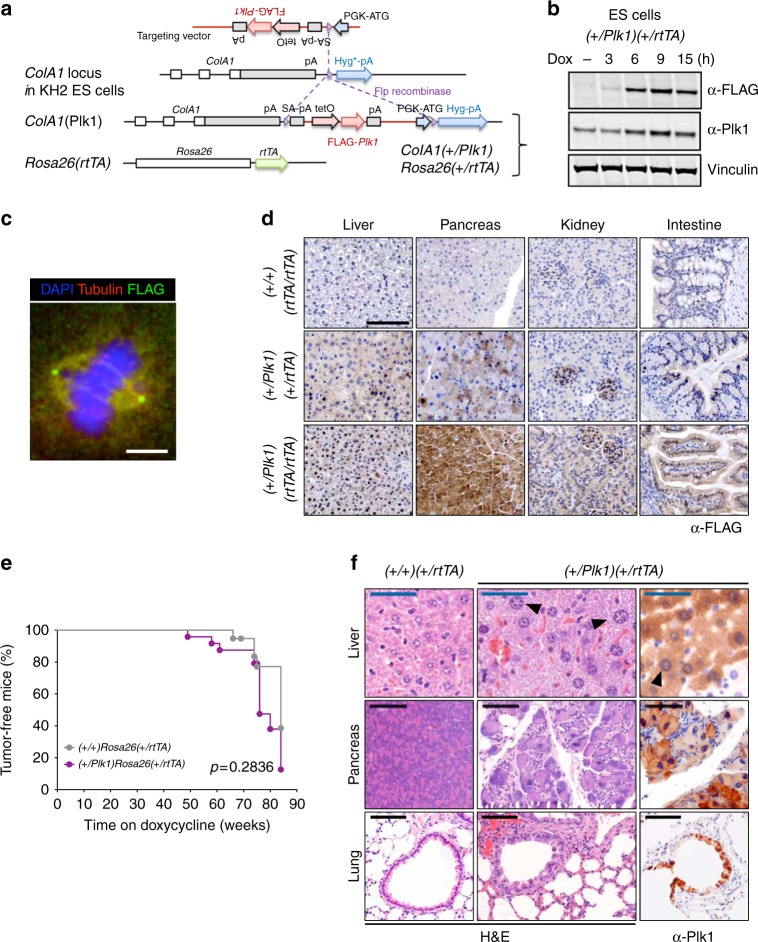
Fig. 1.
Generation of Plk1-inducible mice. a Schematic representation of the alleles used in this work. A cassette containing the human FLAG-Plk1 cDNA downstream of the tetO sequences is inserted in the endogenous ColA1 locus after homologous recombination in KH2 ES cells. This allele [ColA1(Plk1) or (Plk1) in short] is later combined with the Rosa26-rtTA allele expressing the tetracycline transactivator. b (+/Plk1);(+/rtTA) ES cells were treated with Dox and FLAG and Plk1 signal was detected using specific antibodies at the indicated time points. Vinculin was used as a loading control. c Immunofluorescence of (+/Plk1);(+/rtTA) ES cells treated with Dox for 12 h. FLAG (green) is concentrated at the spindle poles with some signal in the spindle microtubules and additional diffuse signal as expected for Plk1. α-tubulin is in red and DAPI in blue. Scale bar 5 μm. d Immunodetection of Flag-Plk1 in the indicated tissues from (+/+);(rtTA/rtTA); (+/Plk1)(+/rtTA) and (+/Plk1)(rtTA/rtTA) mice treated with Dox for 8 weeks. Scale bar 100 μm. e Tumor-free survival of (+/+);(+/rtTA) and (+/Plk1)(+/rtTA) mice fed with Dox since birth during 85 weeks. (+/+)(+/rtTA), 19 mice; (+/Plk1)(+/rtTA), 24 mice. p = 0.2836; Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. f Sections of Dox-treated (+/+);(+/rtTA) and (+/Plk1)(+/rtTA) mice after staining with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or immunodetection of Plk1 (right panel). Cells with abnormally large nuclei are indicated with arrows. Black scale bar: 100 μm, blue scale bar: 50 μm