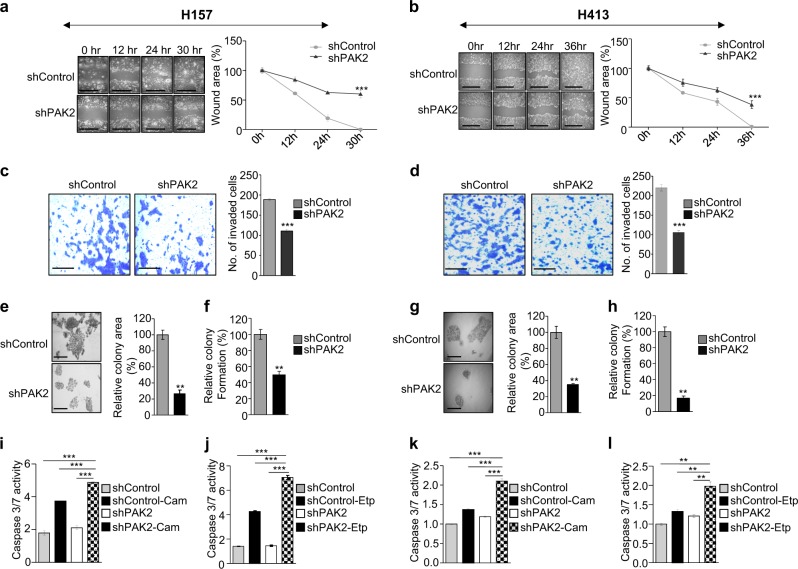
Fig. 3. PAK2 depletion reduces in vitro tumorigenesis of head and neck cancer cell lines.
PAK2 expression was depleted in two types of HNC cell lines (H157 and H413), and key cancer hallmarks were compared in PAK2-depleted and control cells. a, b Cell migration was analyzed through wound healing assay, (left) wound was observed under the microscope, scale bar 500 µm, and (right) quantification of wound width (n = 3). c, d The cell invasion was analyzed through Matrigel invasion assay, (left) single field of invaded cells was captured under the microscope, scale bar: 250 µm, and (right) invaded cells were counted at five different fields under the microscope (n = 3), e, g colony-forming tendency of cells was analyzed, (left) colony size was observed under the microscope, scale bar: 250 µm, and (right) quantification of colony size measured with ImageJ, f, h number of colonies were counted manually after crystal violet staining of the cells (n = 3). The caspase 3/7 activity of i, j H157 cells and k, l H413 cells was analyzed upon treatment with 5 µM camptothecin (Cam) and 50 µM etoposide (Etp) as indicated. Shown results are representative of three independent experiments and f, h are average of three independent experiments. Error bars shows mean values ± SD. Differences were considered statistically significant with **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001