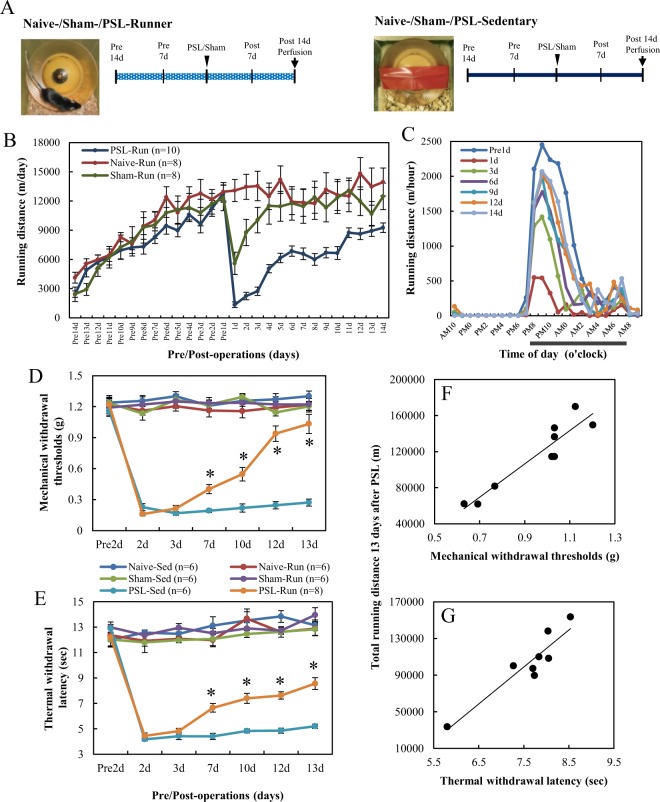
Figure 1.
Changes in running distances and pain behaviors during the VWR period. (A) Protocol of VWR. Naive-, Sham- and PSL-Runner mice were allowed to run freely on the running wheel, whereas Sedentary mice were reared in cages with a locked running wheel. Naive-Runner, Sham-Runner and PSL-Runner mice were placed in individual cages equipped with a low-profile wireless mouse running wheel. (B) Changes in running distances by Runner mice. (C) Changes in diurnal variation in running distances by PSL-Runner mice (n = 7). (D) von Frey and (E) plantar tests were performed for all experimental groups. Mechanical withdrawal thresholds and thermal withdrawal latencies were significantly higher for PSL-Runner mice than for PSL-Sedentary mice (*p < 0.01). Significant positive correlations were observed between total running distances during the 13-day period after PSL, and (F) the withdrawal threshold (R = 0.934, p < 0.001, n = 9) and (G) withdrawal latency (R = 0.929, p < 0.001, n = 8).