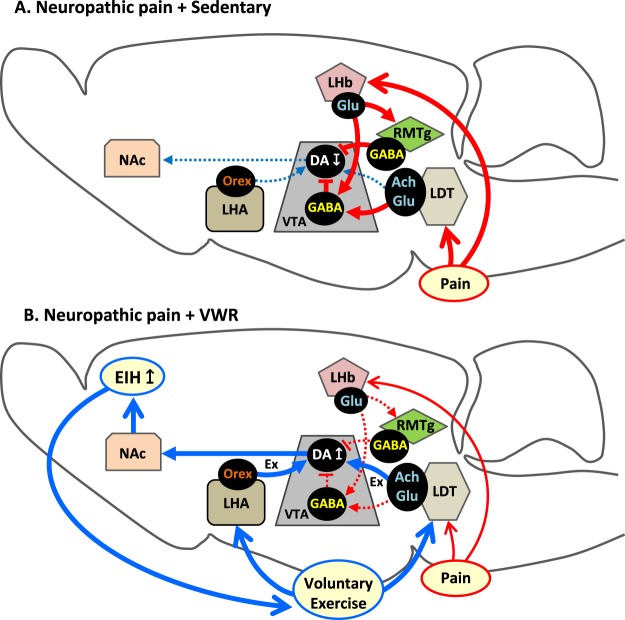
Figure 7.
Potential mechanism of EIH effects following VWR. (A) In NPP + Sedentary mice, pain perception activates RMTg/VTA-GABA neurons via activation of LHb-glutamatergic neurons. LDT neurons also activate VTA-GABA neurons. Activated RMTg/VTA-GABA neurons inhibit VTA-DA neurons, which may promote aversion, depression and reduction of ADL. These changes may function to maintain and deteriorate NPP. (B) In NPP + VWR mice, activation of lVTA-DA neurons via activation of both LDT-cholinergic/glutamatergic neurons and LHA-orexin neurons enhances DA release into the NAc, which may activate the mesolimbic reward system, and thereby produce EIH effects. Creation of positive emotion and pleasure following the attenuation of pain perception reinforces the motivation to perform physical exercise, further enhancing the EIH effects.