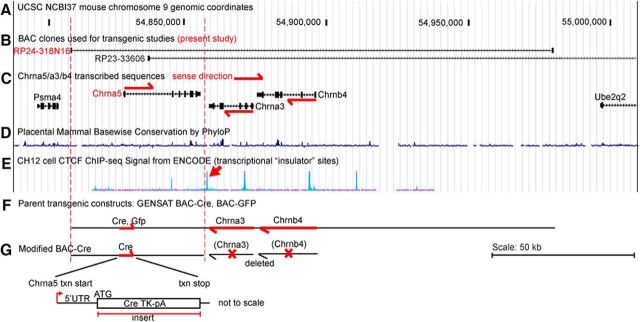
Figure 3.
Structure of the mouse Chrna5/a3/b4 gene cluster and Chrna5-derived transgenic models. The upper section (A–E) shows the structure of the Chrna5/a3/b4 genomic locus and BAC clones within the locus that have been used for transgenic studies. The lower section (F,G) shows the new transgenic construct reported here. The locus structure and design of transgenic constructs is based on NCBI build 37 of the mouse genome. A, Genomic reference coordinates for the Chrna5/a3/b4 locus. B, Location of BACs used, in truncated form, in the present work (RP24-318N16) and in previously reported studies: RP24-318N16 (Hsu et al., 2013), RP23-366O6 (Frahm et al., 2011). C, Location of transcribed genes in and flanking the Chrna5/a3/b4 locus. Chrna5 is transcribed on the forward strand and Chrna3 and Chrnb4 are transcribed on the reverse strand as shown. D, Mammalian species conservation within the locus. E, ChIP-seq data for CTCF transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) in mouse CH12 cells (ENCODE project data from UCSC genome browser). These sites tend to occur at “insulator” sites between independently regulated regions of chromatin. Arrow indicates the CTCF-binding peak used to define the distal end of the Chrna5Cre transgenic construct. F, Structure of the parent BAC-GFP and BAC-Cre constructs from the GENSAT project. G, Structure of the modified BAC-Cre construct used in the present study. Cre recombinase is inserted at the translation start site (ATG) of the Chrna5 gene, disrupting expression of the native gene. Dashed red lines indicate the extent of the transgenic construct in the context of the genomic locus. The transcription start site is indicated by an arrow. The Chrna3 and Chrnb4 transcription units are entirely deleted from the transgenic construct.