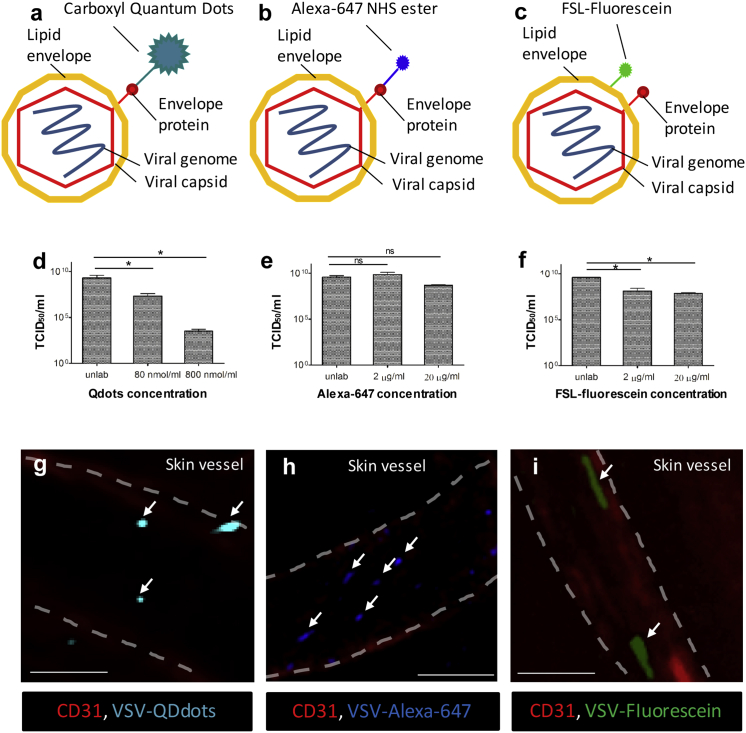
Figure 1.
Labeling Strategies for IVM Tracking of OVs In Vivo
(A–C) Schematic representation of labeling strategies. VSV was labeled using carboxyl quantum dots (Qdots) and Alexa-647 NHS ester (AF647) that covalently bind to superficial amino groups (A and B) or FSL-fluorescein incorporating into lipid membrane (C). (D–F) Virus titers after labeling with low and high concentration of Qdots (D), AF647 (E), and FSL-fluorescein (F) were measured by TCID50 (n = 3). Values represent mean ± SD; *p < 0.05; ns, non-significant. (G–I) In vivo visualization of labeled virus particles within skin blood vessels (red, CD31) using intravital confocal microscopy, immediately following i.v. injection of VSV (5 × 108 PFU) labeled with a high concentration of Qdots (G, 800 nM/mL), AF647 (H, 20 μg/mL), and FSL-fluorescein (I, 20 μg/mL). Vasculature is delineated by white dashed lines, and arrows indicate virus particles. Scale bars, 50 μm; representative images of two independent experiments.