FIG 2 .
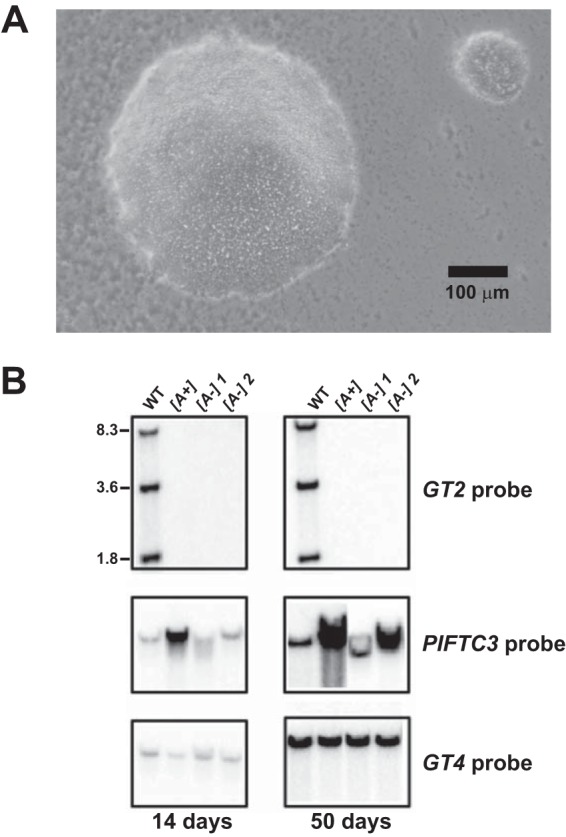
Isolation of Δgt1-3[A-] null mutants lacking the 29-40k amplicon. (A) Microscopic image of an agar plate containing hygromycin-resistant colonies from the second round of targeted gene replacement (see Fig. 1, route 2). Two colonies are shown, of which the one on the top right (diameter, ~130 µm) represents the very small colonies from which Δgt1-3[A-] null mutants were isolated. (B) Genomic Southern blot assays confirming the isolation of Δgt1-3[A-] null mutants and demonstrating the emergence of the 29-40k amplicon in one such line (marked [A-]2) after 50 days in culture. Genomic DNA from wild-type (WT) L. mexicana and Δgt1-3 null mutants initially either containing ([A+]) or not containing ([A-]) the 29-40k amplicon was digested with EcoRI/BglII to release the GT1, GT2, and GT3 genes as separate fragments. The blot was hybridized with probes for the GT2 (top panel), PIFTC3 (middle panel), and GT4 (bottom panel, loading control) genes. Note that substantial sequence identity between GT1, GT2, and GT3 allows the GT2 probe to hybridize to all three genes. The blot on the left represents clonal isolates that had been passaged in liquid culture for 14 days, and the blot on the right represents the same isolates passaged for 50 days. The intensity of the PIFTC3 band increased substantially over the wild-type level in the Δgt1-3[A-]2 line following 50 days in culture.
