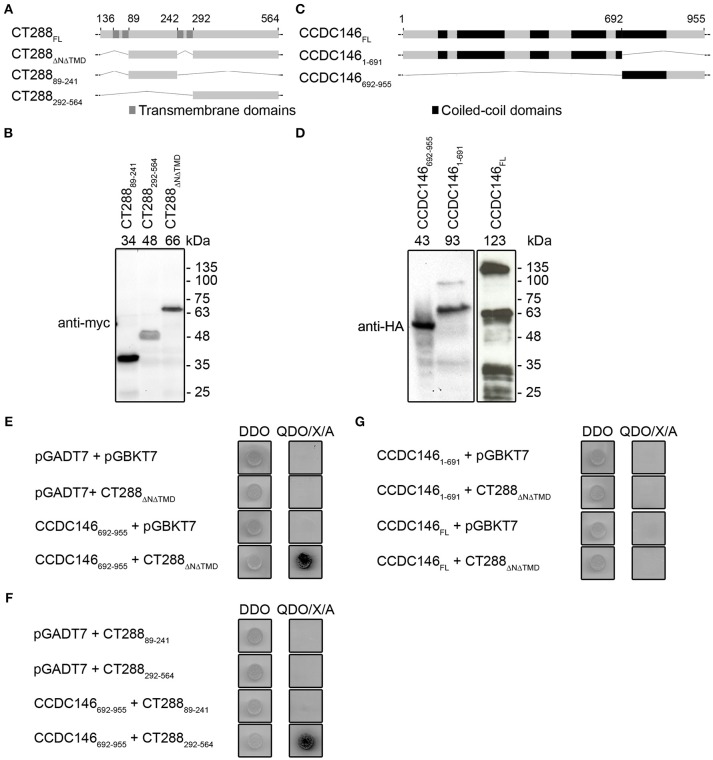
Figure 1.
Chlamydia trachomatis Inc CT288 binds to human centrosomal protein CCDC146 by yeast two-hybrid (Y2H). (A,C) Schematic representation of CT288 and CCDC146 and of the fragments of these proteins used in Y2H assays. The predicted transmembrane domains of CT288 and coiled-coil domains of CCDC146 (as indicated in UniProt Q8IYE0; The UniProt, 2017) are highlighted. (B,D) Immunoblots of protein extracts of S. cerevisiae Y2HGold strains producing (B) myc-tagged fusions of CT288 fragments to the Gal4 DNA-binding domain or (D) HA-tagged fusions of CCDC146 to the Gal4 activation domain. The numbers above the blot indicate the predicted molecular mass of the corresponding fusion proteins. (E) Interaction between CT288ΔNΔTMD and CCDC146692−955 by Y2H. (F) Interaction between CT288292−564 and CCDC146692−955 by Y2H, but not between CT28889−241 and CCDC146692−955. (G) CCDC146FL and CCDC1461−691 do not bind CT288ΔNΔTMD by Y2H. In (E–G), DDO, double dropout media; QDO/X/A, quadruple dropout media supplemented with X-α-Galactosidase and Aureobasidin A (see Materials and Methods;) yeast growth as blue colonies (dark in the image) in high stringency QDO/X/A media indicates a protein-protein interaction. The empty pGADT7 and pGBKT7 plasmids were used as controls in the Y2H assays.