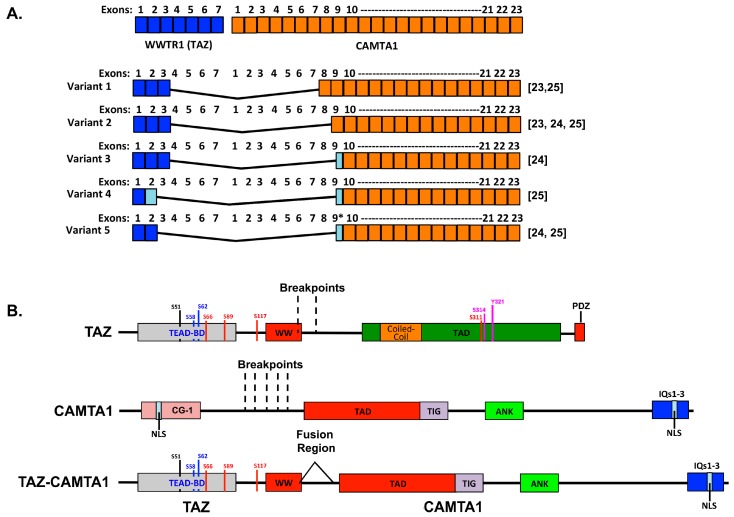
Figure 1.
Schematic of the WWTR1–CAMTA1 fusions and their protein structures. (A) Shown is the exonic structure of the WWTR1 and CAMTA1 transcripts (top) as well as the fusion transcripts identified in the literature to date [23,24,25]. Light blue boxes indicate partial exons. (B) Protein structures for TAZ, CAMTA1, and the fusion with key domains indicated. TEAD-BD, TEAD binding domain; WW, WW domain; TAD, transactivation domain; PDZ, PDZ binding motif; CG-1, CG-1 DNA binding domain; NLS, nuclear localization signal; TIG, transcription factor immunoglobulin domain; ANK, ankyrin repeats; IQ, IQ calmodulin-binding motifs. Regulatory phosphorylation sites on TAZ are also shown: S66, S89, S117, and S311 are LATS phosphorylation sites; S58 and S62 are glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta phosphorylation sites; S51 is critical for TEAD binding; S314 is a CK1ε/δ kinases phosphorylation site; and Y321 is a Src family kinase/Abl kinase phosphorylation site.