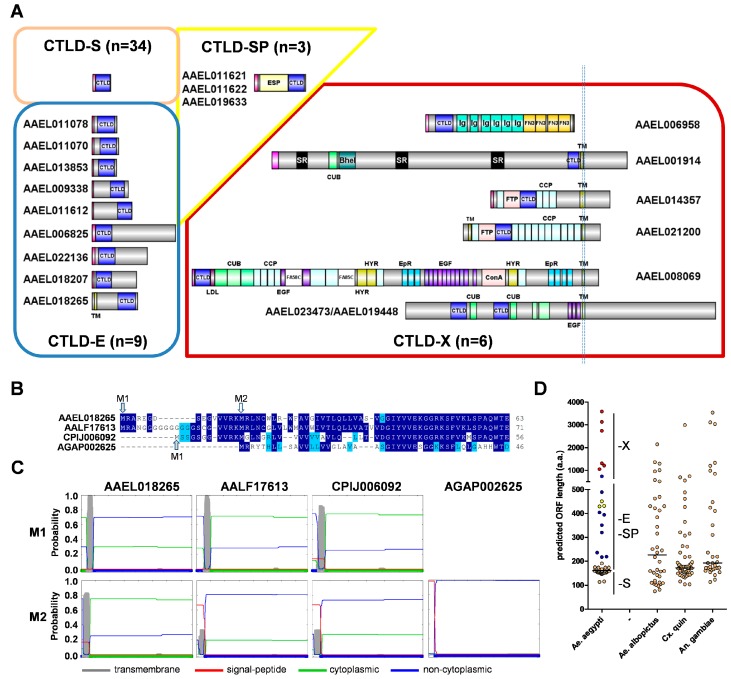
Figure 1.
A. aegypti C-type lectin domain containing proteins (CTLDcps). (A) Primary structure and categorization of CTLDcps. CTLD-S (orange box), CTLD-E (blue box), CTLD-SP (yellow box), and CTLD-X (red box) are indicated. All of the models were drawn to scale using IBS v1.0.3. Predicted signal peptides are indicated at the N-terminus of each sequence (pink), along with predicted transmembrane spanning domains (TM; gold), CTLD (dark blue), and elastase-serine protease (ESP). For CTLD-X members, domains are as indicated and the reader is directed to supplemental Table S1 for a full list of domains including accession numbers for each; (B) Alignment of the N-terminus of CTLD-E gene AAEL018265 and its orthologs from other mosquitoes. Identical (dark blue) and similar (light blue) residues are indicated. Initiation methionine (M1) and alternative methionine (M2) are indicated; (C) Signal Peptide/transmembrane domain prediction output from Phobius [14] for CTLD-E gene AAEL018265 and its orthologs based on the M1 or M2 methionines; and, (D) Predicted amino acid lengths of CTLD genes in A. aegypti and three other mosquitoes, by category. For A. aegypti, CTLD-S (orange), CTLD-E (blue), CTLD-SP (yellow), and CTLD-X (red) groups are indicated. Horizontal line indicates the median length.