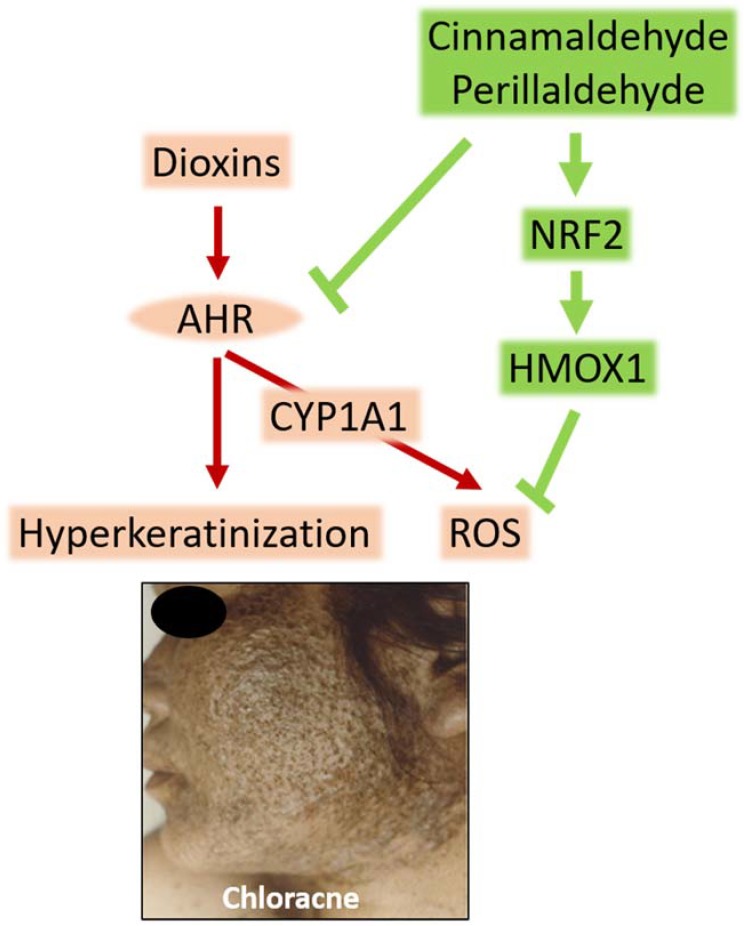
Figure 1.
Dioxins activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), upregulate the expression of cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1), and generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in keratinocytes and sebocytes. The ligation of AHR by dioxins also accelerates terminal differentiation. Oxidative stress and hyperkeratinization are probably responsible for chloracne. Cinnamaldehyde (a functional component of C. cassia) and perillaldehyde (a functional component of P. frutescens) are potent inhibitors of AHR–CYP1A1 signaling. On the other hand, they activate nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (NRF2). NRF2 is a master switch for the cellular antioxidative system. The activation of NRF2 upregulates various antioxidative enzymes, such as heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1), and neutralizes ROS. These natural phytochemicals are useful for managing chloracne.