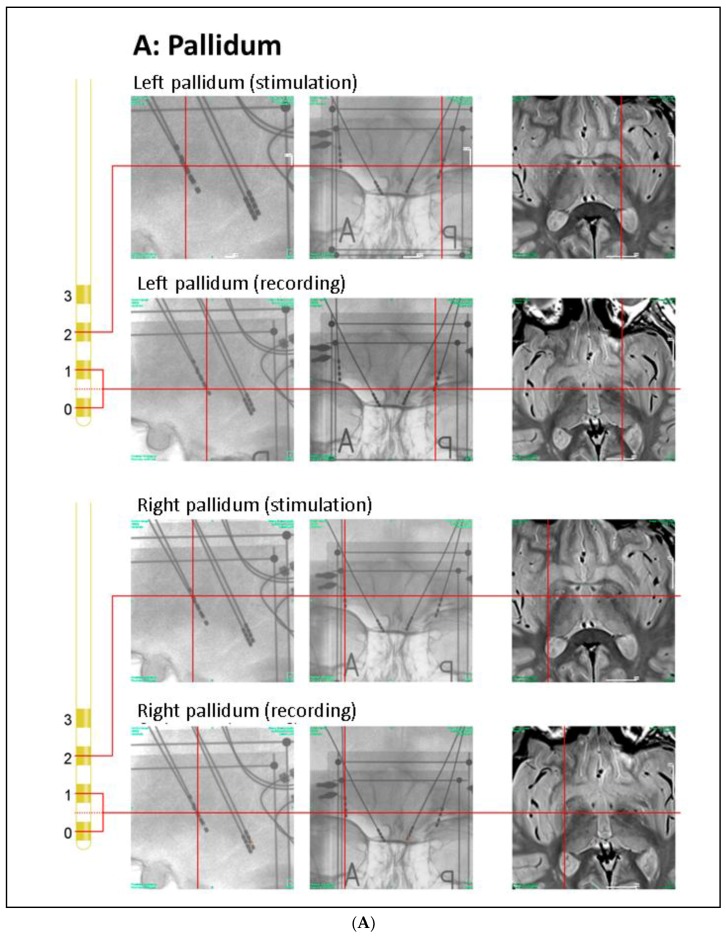
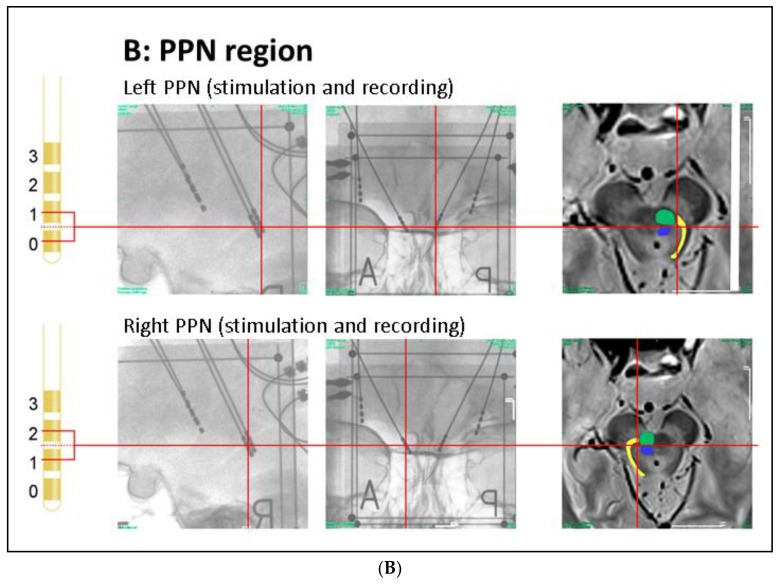
Figure 1.
Anatomical positions of DBS electrodes. (A) Anatomical location of the GPi electrodes as determined by intra-operative orthogonal x-ray imaging: in the lateral and frontal x-ray views, the location of each contact used for stimulation or recording is marked by a red cross, as is the corresponding location in the proton weighted MRI (from left to right). Orthogonal x-ray images and intra-operative CT were acquired with stereotactic image fiducials allowing for transformation into a common (stereotactic) coordinate system with a spatial mismatch between CT and x-ray coordinates of less than 1 mm (unpublished data). MRI images were transformed into this coordinate system by manual image registration to the CT data using anatomical landmarks. Contacts 0–2 of the left electrode and contacts 0 and 1 of the right electrode were located within the ventro–postero–lateral section of the respective GPi. Please note that LFP signals were recorded and analyzed both from electrode pairs 0–1 and 2–3 (during contralateral stimulation); (B) Anatomical location of the PPN electrodes: the PPN region is located lateral to the decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles (green) and the central segmental tract (blue) and medial to the lemniscal systems (yellow) (see Zrinzo et al., 2008 for anatomical details). According to these landmarks, contacts 0–2 of the left electrode and contacts 1 and 2 of the right electrode were located within the respective rostral PPN. Abbreviations: CT: computer tomography, DBS: deep brain stimulation, GPi: globus pallidus internus, MRI: magnetic resonance imaging, PPN: pedunculopontine nucleus region.