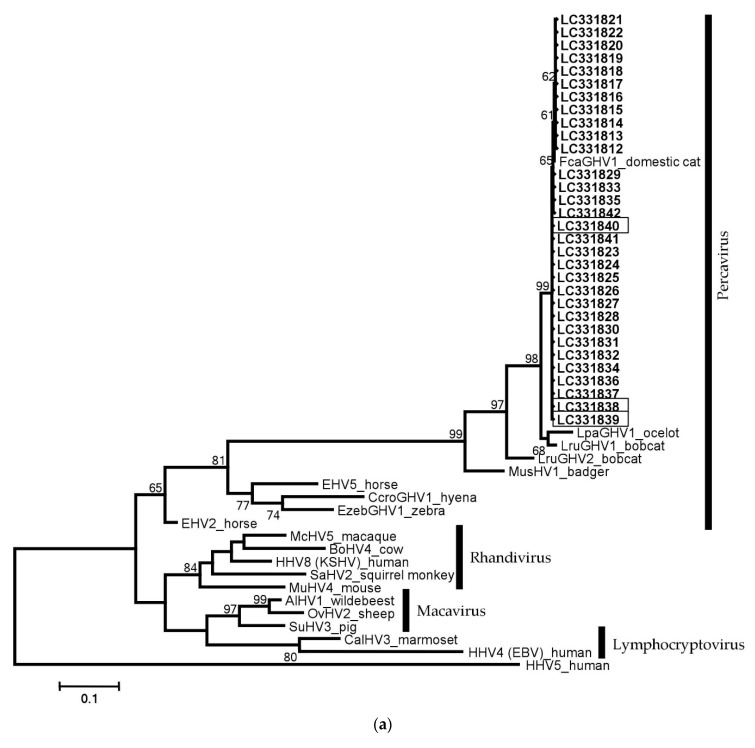
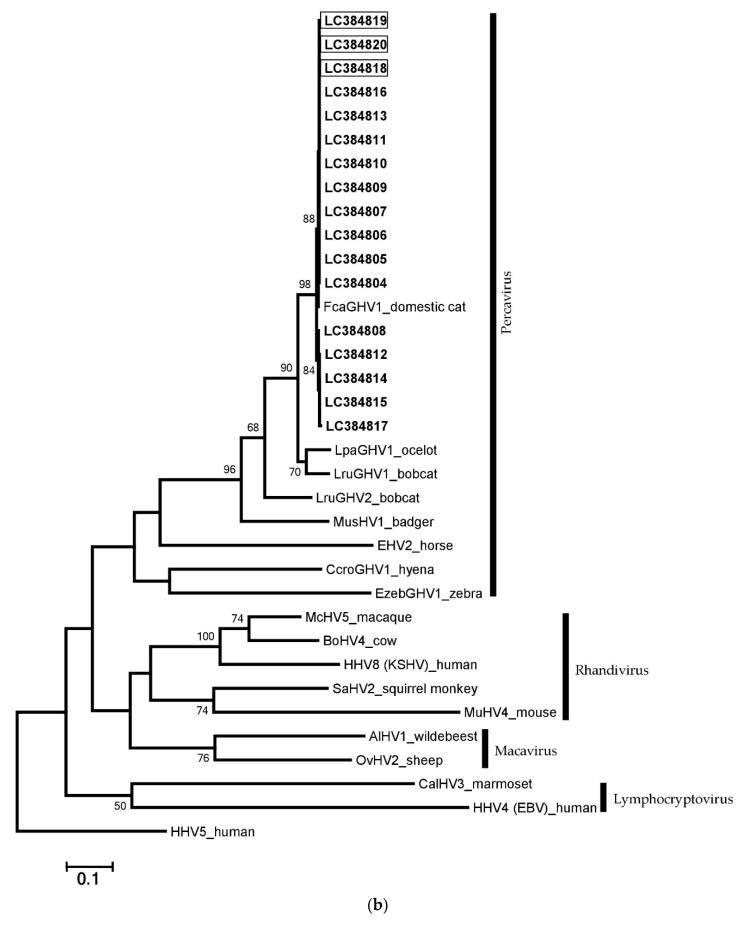
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of gammaherpesviruses (GHVs) using glycoprotein B and DNApol nucleotide alignments. The trees display multiple GHV nucleotide sequences, and betaherpesvirus human cytomegalovirus (human herpesvirus 5; GenBank accession no. NC006273) represents the outgroup. (a) The 31 clones of FcaGHV1 gB detected in this study are shown in bold (LC331812–LC331842) including three clones isolated from TLCs (indicated with boxes); (b) The 17 clones of FcaGHV1 DNApol identified in this study are shown in bold (LC384804–LC384820) including three clones isolated from TLCs (indicated with boxes). Maximum-likelihood analysis was performed, and the Kimura 2-parameter model was used to calculate the distance matrix of the aligned sequences, with all branch lengths measured as the number of substitutions per site. Bootstrap support out of 100 replicates is shown for each branch node (values of <50 are not displayed). Virus names, definitions and the GenBank accession numbers of the sequences used in the phylogenetic trees are as follows: Human herpesvirus 4 (HHV4, Epstein–Barr virus, NC007605); Callitrichine herpesvirus 3 (CalHV3, NC004367); Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 (AlHV1, NC002531); Ovine herpesvirus 2 (OvHV2, NC007646); Mustelid herpesvirus 1 (MusHV1, AF376034); Felis catus gammaherpesvirus 1 (FcaGHV1, KF840715); Lynx rufus gammaherpesvirus 1 (LruGHV1, KF840716); Leopardus pardalis (LpaGHV1, KP721220); Lynx rufus gammaherpesvirus 2 (LruGHV2, KP721221); Bovine herpesvirus 4 (BoHV4, NC002665); Saimiriine herpesvirus 2 (SaHV2, NC001350); Suid herpesvirus 3 (AF478169); Equid herpesvirus 2 (EHV2, NC001650); Equid herpesvirus 5 (EHV5, AF050671); Crocuta crocuta gammaherpesvirus 1 (CcroGHV1, DQ789371); Equus zebra gammaherpesvirus 1 (EzebGHV1, AY495965); Macacine herpesvirus 5 (McHV5, NC003401); Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8, Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, NC009333) and Murid herpesvirus 4 (MuHV4, NC001826).