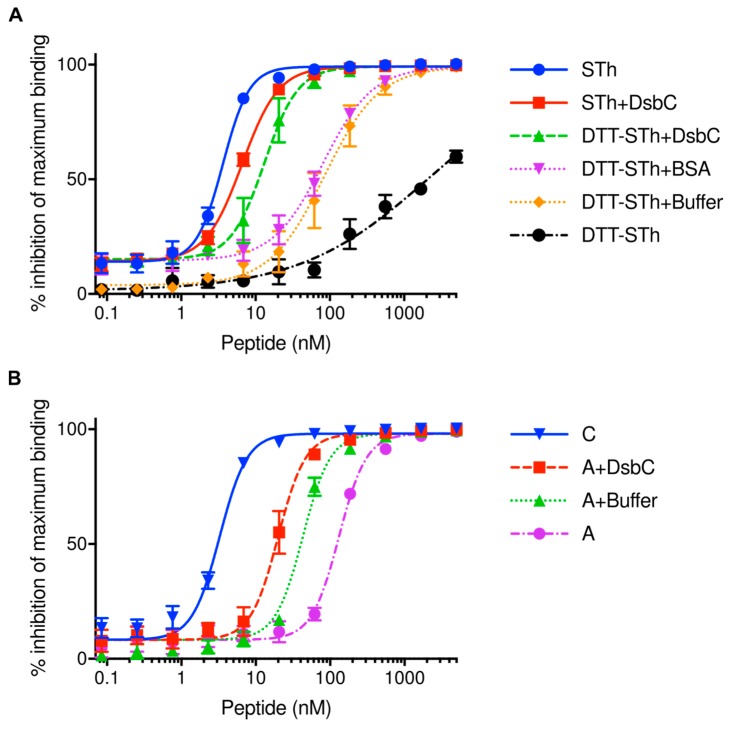
Figure 3.
DsbC assisted refolding of STh. (A) STh was denatured with DTT and heat and subjected to different refolding conditions. The effect of refolding was monitored using the competitive C30 mAb ELISA. Three independent ELISAs were performed. Explanation of legends with calculated IC50s (nM): STh, STh peptide purified using the DsbC-His-TEV system (3.6 ± 0.2); DTT-STh, denatured STh (2111 ± 250); DTT-STh+Buffer, DTT-STh incubated in GSH/GSSG buffer containing reduced and oxidized glutathione (85 ± 5); DTT-STh+BSA, DTT-STh incubated with BSA in GSH/GSSG buffer (81 ± 6); DTT-STh-DsbC, DTT-STh incubated with DsbC in GSH/GSSG buffer (13 ± 1); STh+DsbC, STh incubated with DsbC in GSH/GSSG buffer (6.6 ± 0.4). (B) Refolding of the STh peptide from peak A compared to correctly folded STh (peak C; Figure 2A) monitored using the competitive C30 mAb ELISA. Three independent ELISAs were performed. Explanation of legends with calculated IC50s (nM): A, STh peptide from peak A (132 ± 6); A+Buffer, A incubated in GSH/GSSG buffer containing reduced and oxidized glutathione (43 ± 2); A+DsbC, A incubated with DsbC in GSH/GSSG buffer (20 ± 1); C, STh peptide from peak C (3.26 ± 0.2). The analysis in figure (A,B) was performed with serial dilutions of the peptides (horizontal axis; logarithmic scale). The symbols represent mean values of three independent experiments, and the error bars depict standard deviations.