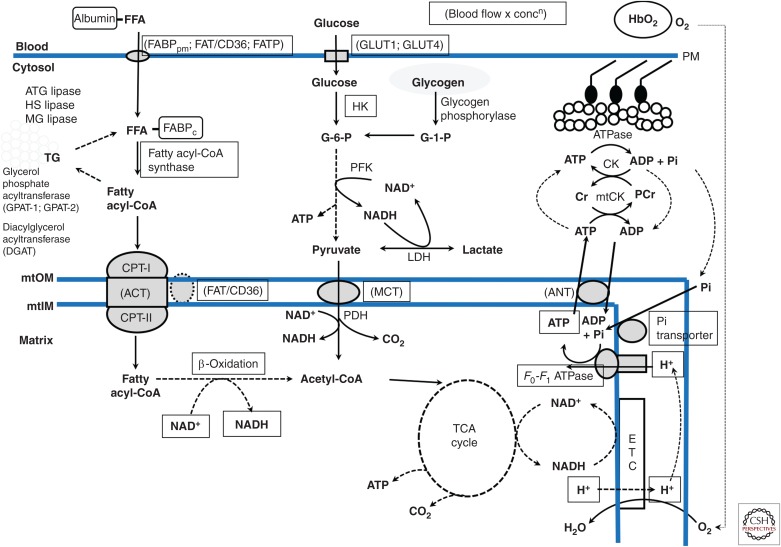
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of skeletal muscle metabolism. Hb, Hemoglobin; FFA, free fatty acid; FABPpm and FABPc, fatty acid binding protein–plasma membrane and cytoplasm; FAT/CD36, fatty acid translocase; FATP, fatty acid transport protein; GLUT1 and 4, glucose transport proteins 1 and 4; PM, plasma membrane; ATG, HS, and MG lipases, adipocyte glyceride, hormone-sensitive, and monoglyceride lipases; mtOM and mtIM, outer and inner mitochondrial membranes; CPT-I and -II, carnitine palmitoyl transferase I and II; ACT, acylcarnitine transferase; G-1-P and G-6-P, glucose 1 and 6 phosphate; HK, hexokinase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase, MCT, monocarboxylate transport proteins; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; ANT, adenine nucleotide transport protein; Cr and PCr, creatine and phoshocreatine; CK and mtCK, creatine kinase and mitochondrial CK.