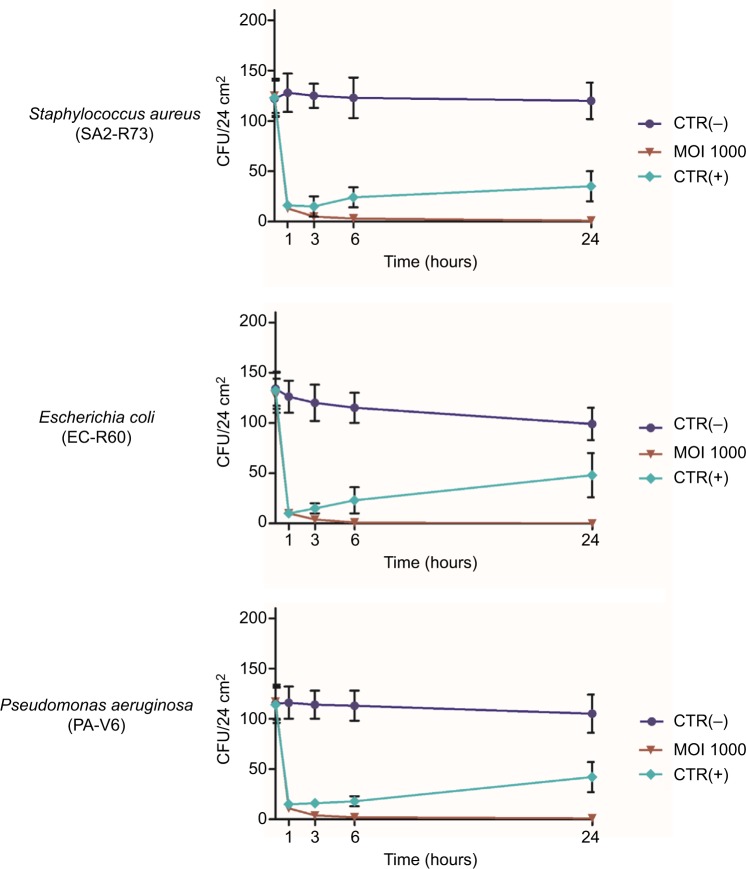
Figure 3.
Reduction of MDR hospital isolates on hard surfaces treated with specific phages. One hundred CFU of each bacterial isolate (wild-type S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa strains) were spread on ceramic, plastic, or glass surfaces, allowed to dry, and subsequently treated with the specific phages, suspended in PBS, at 1000 MOI. After 1, 3, 6, and 24 hours at room temperature, residual viable cells were measured by Rodac sampling with specific selective media, and subsequent CFU count after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C. Negative CTR(−) samples were treated with PBS alone. Positive CTR(+) samples were treated with denatured alcohol. Results represent the mean of triplicate samples in two independent experiments, for each surface type. As no significant differences were observed between surface types, graphed values represent the mean ± SD of all the measured samples (18 total samples).
Abbreviations: MDR, multidrug-resistant; CFU, colony forming units; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; MOI, multiplicity of infection; CTR, control.