Figure 5.
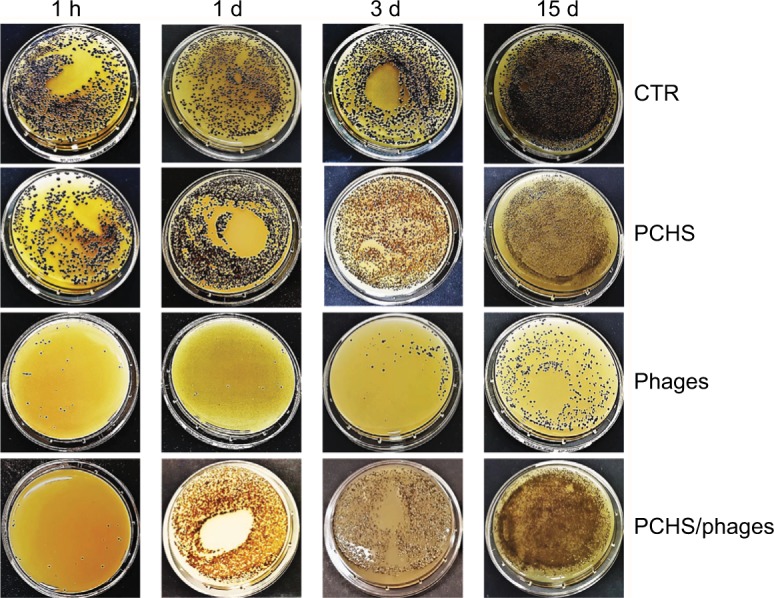
Reduction of Staphylococcus aureus contamination in situ, by a combined phage–probiotic detergent. About 100 CFU of S. aureus (ATCC strain) per 24 cm2 were uniformly spread on the surface of a ceramic sink. After 24 hours, the artificially contaminated surface was treated with water (CTR), probiotic detergent alone (PCHS), anti-staphylococcal phages in PBS alone (phages), or probiotic detergent including anti-staphylococcal phages (PCHS + phages). Phages were used at 1000 MOI. After 1 hour, and 1, 3, and 15 days, surfaces were sampled by Baird–Parker Rodac plates, and residual S. aureus viable cells were counted by enumerating black round colonies after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C. PCHS-Bacilli gave rise to gray-brown irregular colonies on Baird–Parker medium, easily distinguishable from the S. aureus ones. Results are representative of duplicate samples in three independent experiments.
Abbreviations: h, hours; d, days; ATCC, American Type Culture Collection; PCHS, Probiotic Cleaning Hygiene System; CFU, colony forming units; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; MOI, multiplicity of infection; CTR, control.
