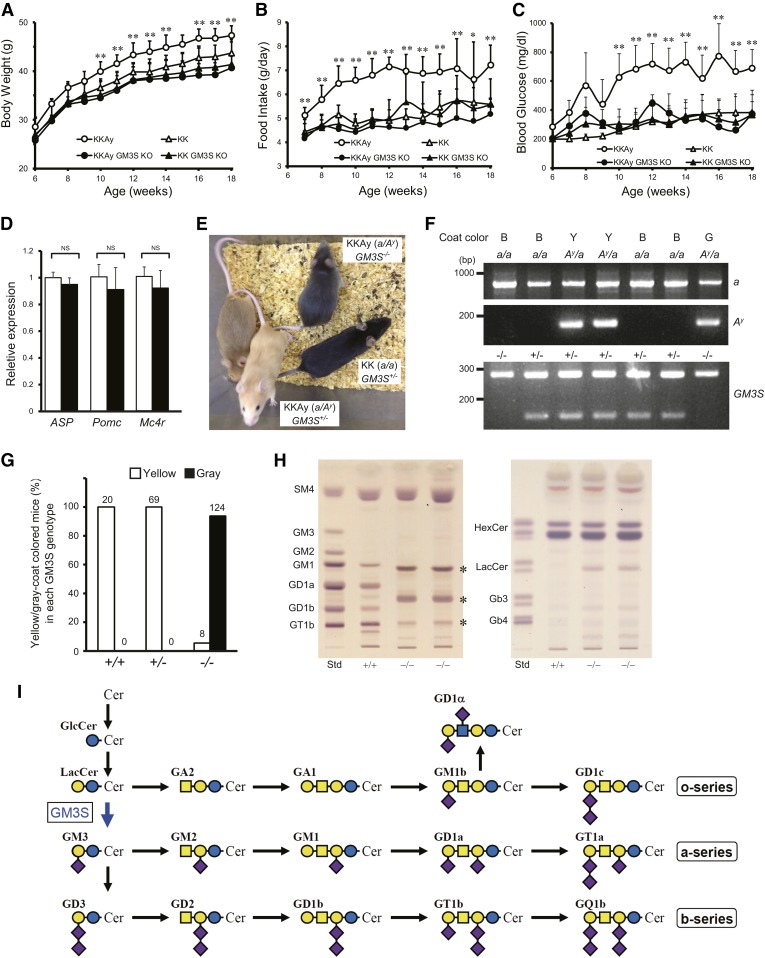
Fig. 1.
GM3S KO prevented development of hyperphagia and obesity in KKAy mice. A–C: Body weight (A), food intake (B), and nonfasting blood glucose levels (C) of KKAy and KK mice with or without deletion of the GM3S gene (GM3S KO) (n ≥ 5 for each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus KKAy GM3S KO. D: Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA for ASP, Pomc, and Mc4r in KKAy and KKAy GM3S KO hypothalami. White bar, KKAy; black bar, KKAy GM3S KO (n = 3 for each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus KKAy GM3S KO. E: Coat color phenotype of GM3S KO (GM3S−/−) observed in the KKAy (a/Ay) background. F: Representative genotyping PCR results for KKAy GM3S KO mice. Top panel: Genotyping results for the a/Ay allele. The a and Ay alleles generate PCR products of 839 bp and 163 bp, respectively. Coat color: B, black; Y, yellow; G, gray. Bottom panel: Genotyping results for GM3S KO. The WT and mutant alleles generate PCR products of 276 bp and 120 bp, respectively. G: The percentage of yellow- or gray-coat-colored offspring compared with the total number of Ay/a offspring born with each GM3S genotype. The number of each group is indicated on the top of each bar. Because of the infertility of KKAy females, KKAy males (Ay/a, GM3S+/− or −/−) and KK females (a/a, GM3S+/− or −/−) were used for breeding. Data of the a/a offspring (black coat color) were excluded. H: TLC of acidic (left) and neutral (right) GSLs from KKAy (+/+) and KKAy GM3S KO (−/−) brains. GSLs were detected using orcinol-sulfuric acid reagent. The asterisks indicate o-series gangliosides whose biosynthesis is independent of GM3S [see text and references (5) and (17) for details]. (I): Biosynthetic pathway of ganglio-series gangliosides. GM3S is a sialyltransferase required for initiation of synthesis of a- and b-series gangliosides.