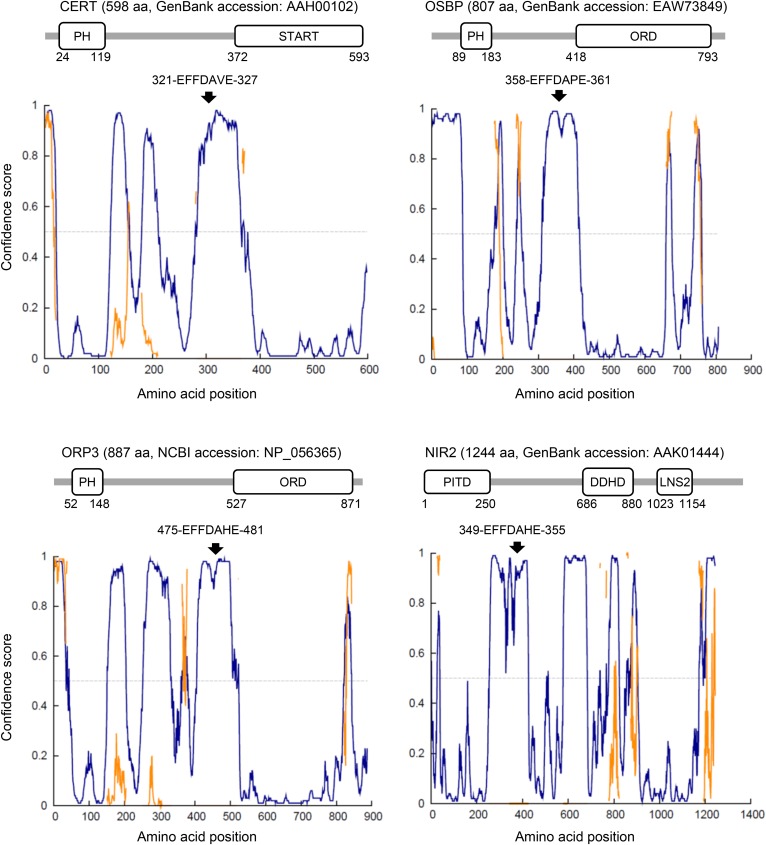
Fig. 3.
Canonical FFAT motifs localize in disordered regions between structured domains in LTPs. Intrinsic disorder profiles in LTPs with canonical FFAT motifs were analyzed using the DISOPRED3 program (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/?disopred=1), while domains in the LTPs were analyzed using the SMART program (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) using amino acid sequences from the databank accession number as queries. The start and end amino acid positions of FFAT motifs and globular domains in the proteins are specified in each panel. Nir2 is also known as membrane-associated PITP1 (PITPNM1). Note that the LNS2 domain in human Nir2 was assigned to residues 980–1115 in a previous study (104), while it was assigned to residues 1023–1154 in the search with the SMART program. In addition, a DAG-binding-like segment identified in the previous study (104) was not found in the search with the SMART program. PITD, PI-transfer domain. In the intrinsic disorder profiles: blue line, region with a disordered state; orange line, region with protein-binding activity; arrow, amino acid position of canonical FFAT motifs. FFAT motifs in LTPs localize to disordered regions between structured domains. The motif location may restrict the structured domains within a limited distance from the FFAT/VAP-mediated ER contact sites with appropriate topology.