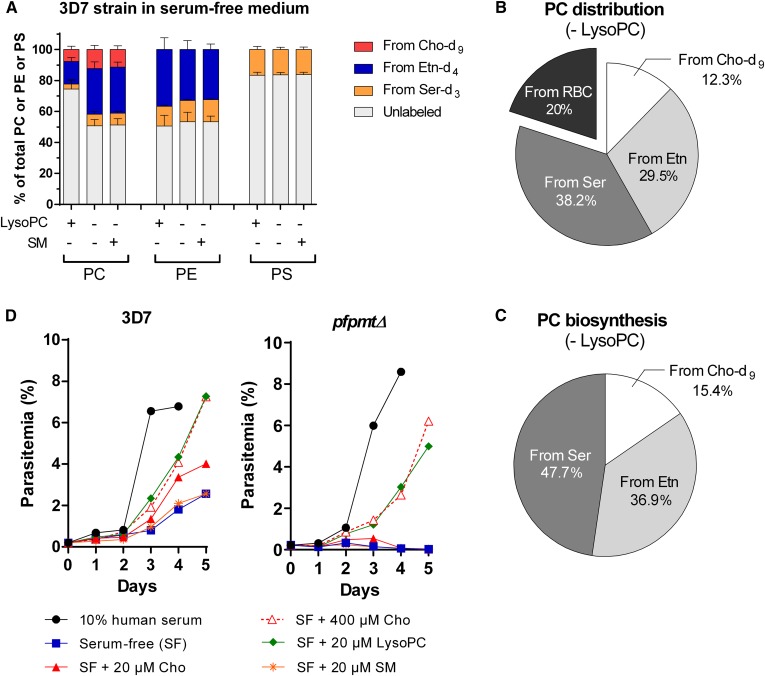
Fig. 4.
Influence of PMT and LysoPC on PC biosynthesis in P. falciparum. A: Contributions of Cho-d9, Etn-d4, and Ser-d3 to biosynthesis of PL in the P. falciparum 3D7 strain. P. falciparum-iRBCs were incubated for 48 h in serum-free medium with 20 µM Cho-d9, 10 µM Etn-d4, and 140 µM Ser-d3 and supplemented or not with 20 µM LysoPC or 20 µM SM. After incubation, PLs were quantified by LC/MS/MS. Results are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). B, C: Relative precursors contribution to PC content (B) and biosynthesis (C) in the absence of LysoPC. P. falciparum-iRBCs were incubated for 48 h in serum-free medium with 20 µM Cho-d9, 10 µM Etn-d4, and 140 µM Ser-d3. Results are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). D: Effect of LysoPC on growth of 3D7 and pfpmtΔ strains. P. falciparum-iRBCs were cultivated in culture medium supplemented with 10% human serum (control) or in serum-free medium supplemented or not with 20 µM Cho, 400 µM Cho, 20 µM LysoPC, or 20 µM SM. One representative experiment (of at least three experiments) is shown.