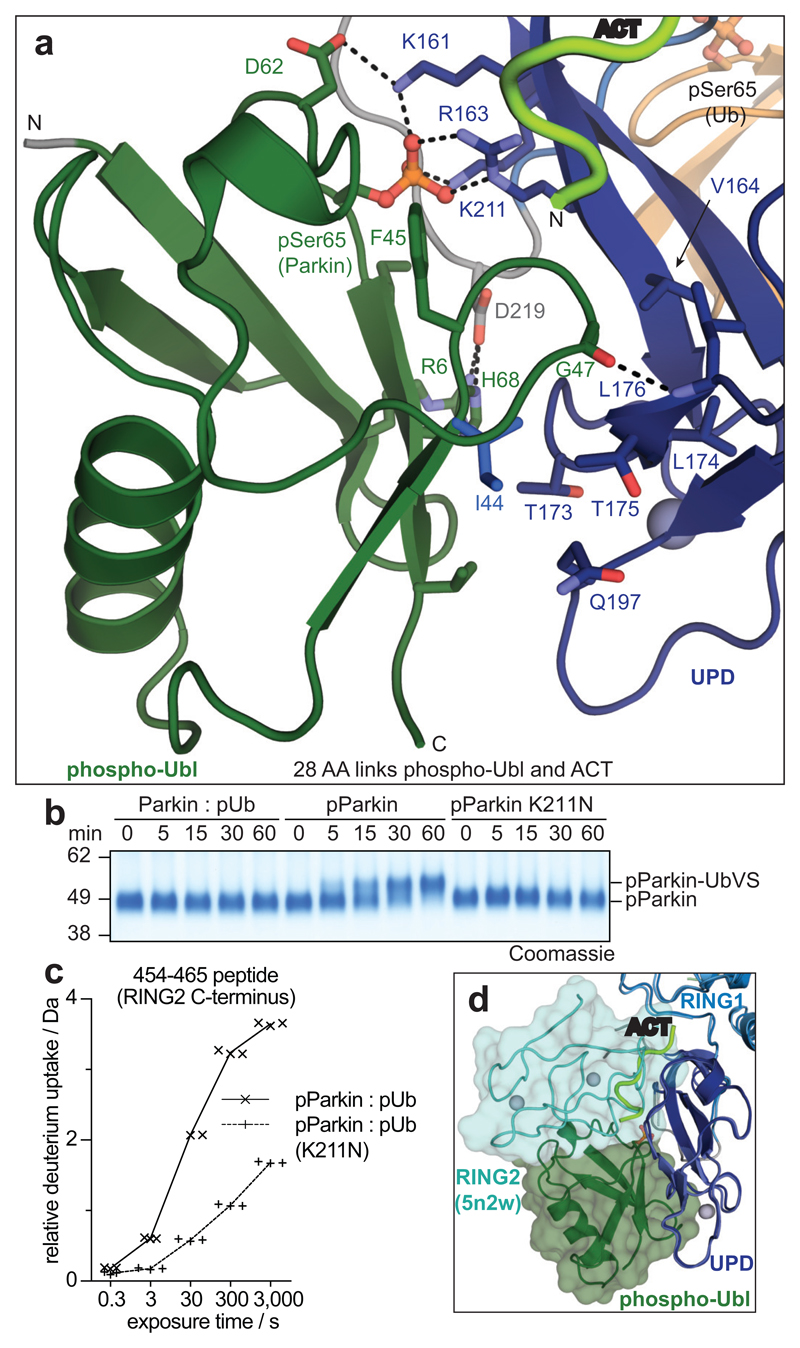
Figure 3. The Parkin UPD - phospho-Ubl interaction.
a, Structural detail of the binding site between Parkin phospho-Ubl (green) and UPD (blue). Key residues are shown, and phospho-Ser65 is highlighted. Grey spheres indicate Zn atoms, and hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. b, Ub-VS probe reactivity of the RING2 catalytic Cys residue with Parkin:phospho-ubiquitin, phospho-Parkin, or phospho-Parkin K211N. The experiment was done in duplicate with identical results, for gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. c, HDX-MS analysis of phospho-Parkin:phospho-ubiquitin in comparison to phospho-Parkin K211N:phospho-ubiquitin. The C-terminal peptide profiles are compared, see Extended Data Fig. 7d for overall data. The RING2 C-terminus remains solvent protected in the phospho-Parkin K211N background. Technical triplicates are shown for all time points. d, Superposition of Parkin-pUb (5n2w, 6), and phospho-Parkin-pUb showing relative positions of the RING2 (cyan surface) and phospho-Ubl (green surface), respectively, on the UPD domain.