Table 1. CB1 and CB2 receptor affinity of 1,3,4- and 1,2,4-oxadiazole regioisomers 1a–c and 9a–c.

| |||||
| Compd | R | X | Y | K i (hCB2) ± SEM a [nM] | Displacement (hCB1) b |
| 1a |

|
Br | F | 2.9 ± 0.41 d | –13% c |
| 1b | F | Br | 6.7 ± 1.0 d | –5% | |
| 1c | CN | F | 270 ± 32 d | –8% | |
| 9a |
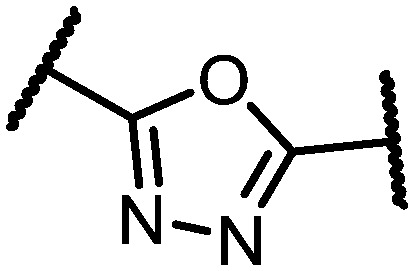
|
Br | F | 25 ± 4.1 | 22% c |
| 9b | F | Br | 318 ± 55 | –8% | |
| 9c | CN | F | 219 ± 16 | –1% | |
| CP 55940 | 8.44 ± 0.18 | 9.26 ± 0.12 | |||
| WIN 55212-2 | 8.57 ± 0.16 | 8.72 ± 0.24 | |||
| HU 210 | 9.78 ± 0.04 | 9.55 ± 0.06 | |||
aThe reported Ki-values are mean values of three independent experiments (n = 3).
bDue to the low hCB1 affinity, only the radioligand displacement at a test compound concentration of 1 μM is given as mean value of two independent experiments (n = 2).
cMean value of four experiments (n = 4).
dThe CB2 affinity of lead compounds 1a–c has been recorded previously in another laboratory.11
