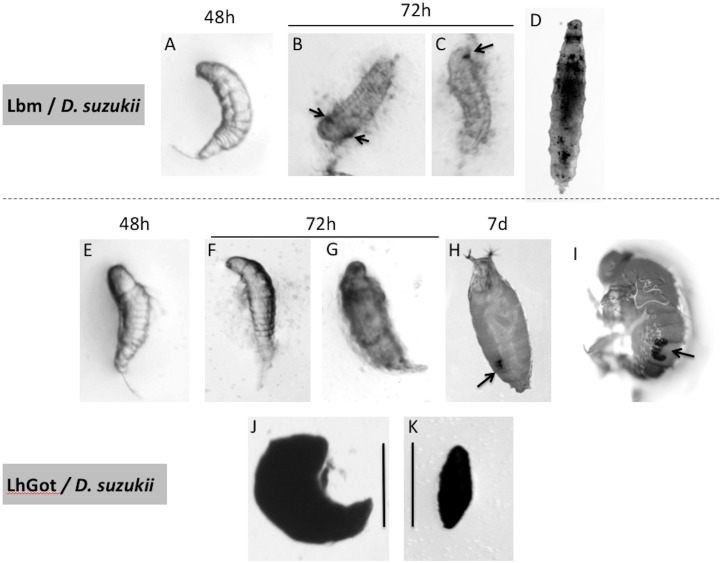
Fig 3. Timing of encapsulation of L. boulardi Ism (Lbm) and L. heterotoma Gotheron eggs in D. suzukii larvae.
Host larvae were observed and/or dissected at different times following parasitism by L. boulardi ISm (Lbm) (A-D) or L. heterotoma Gotheron (E-I). 48h post-parasitism, free-living larvae were mainly observed for the two parasitoids (A and E). At 72h, Lbm larvae were entangled in a thin layer of cells, and a few melanization spots (arrows) were observed (B, C), whereas only a few cells were found on L. heterotoma larvae, without melanization (F, G). Most larvae parasitized by Lbm showed an over-melanization response, and the fly was unable to pupate and died (D). Surviving larvae parasitized by L. heterotoma continued to develop and pupae (H) and emerged adult flies contained a capsule (I). The size of the capsule formed by D. suzukii against L. heterotoma (J) and by D. melanogaster YR against L. boulardi ISy (Lby) (K) are compared. Bar is 0.2 mm.