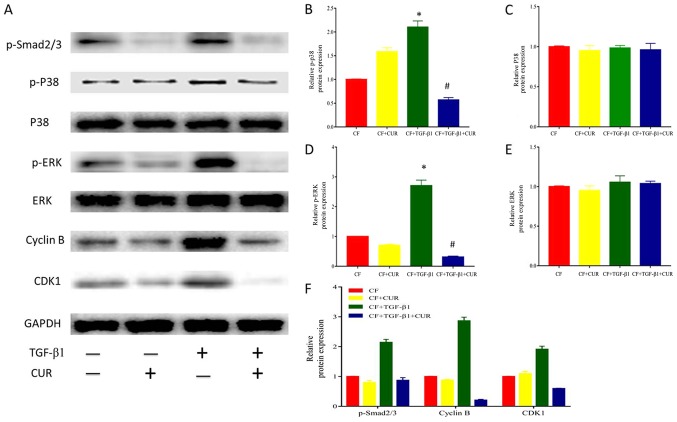
Figure 4.
CUR affects cell-cycle protein expression by inhibiting p38 MAPK signaling activation in TGF-β1-induced CFs. (A) Western blotting analysis of p-smad2/3, P38, p-P38, ERK, p-ERK, Cyclin B, and CDK1 expression. Quantitative analysis of (B) p-P38 protein expression using P38 as a control, (C) P38 protein expression using GAPDH as a control, (D) p-ERK protein expression using ERK as a control, (E) ERK protein expression using GAPDH as a control, and (F) p-smad2/3, Cyclin B and CDK1 protein expression using GAPDH as a control. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate experiments. *P<0.05 vs. CF group; #P<0.05 vs. CF + TGF-β1 group. CUR, curcumin; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TGF, transforming growth factor; CFs, cardiac fibroblasts; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p-, phosphorylated; CDK, cyclin dependent kinase; smad2/3, phosphorylation-mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2/3.