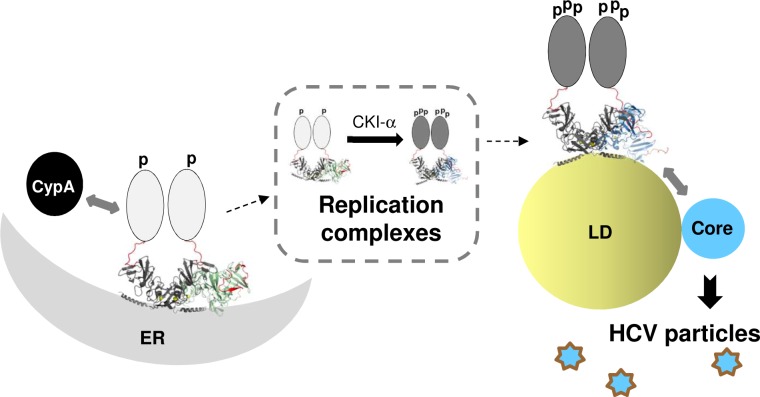
Fig 13. A model of functional role of NS5A oligomers during HCV replication.
Oligomerization of NS5A may stabilize certain NS5A conformation allowing its interaction with CypA, which, together with NS5A oligomers, promote HCV replication complex (RC) formation. Interaction between NS5A and other HCV nonstructural proteins in the RC should then allow the access of kinases to hyperphosphorylate NS5A, which promotes NS5A association with LD and permits its interaction with core leading to infectious HCV production. See the discussion for detail. Hypothetical tetrameric arrangement of two heteromeric dimer forms of NS5A-DI (PDB-1ZH1 and PDB-3FQM) binding to negative curvature of ER at the left side and that of two homodimers (from PDB-1ZH1) binding to positive curvature of LD surface at the right are shown. The C-terminal tail portion is highlighted in red color in the structure to show the location and orientation of this region relative to the membrane surface. Artificial oval drawing representing the unstructured NS5A-DII and DIII were placed only on one of two dimers. The “p” and “ppp” represent hypo- and hyper-phosphorylated NS5A.