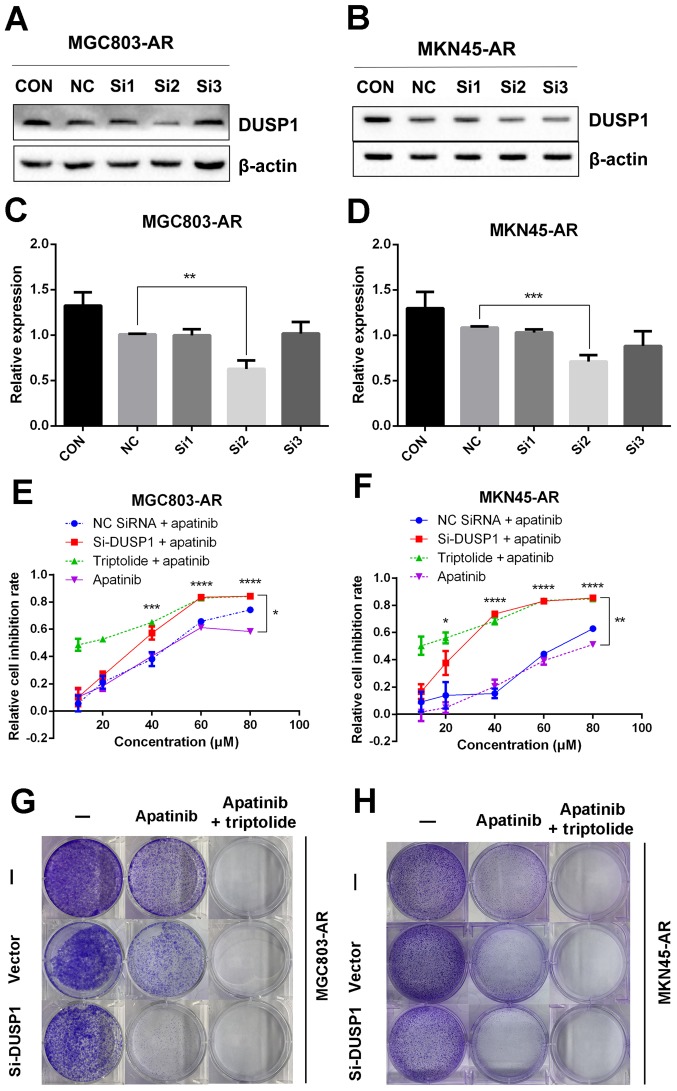
Figure 5.
Knockdown of DUSP1 overcomes Apa resistance. (A) MGC803-AR and (B) MKN45-AR cells were treated with siRNA targeting DUSP1 (clones Si1, Si2 and Si3), and expression of DUSP1 was evaluated by western blot analysis. β-actin served as a loading control. Histograms represent the relative quantitative expression in (C) MGC803-AR and (D) MKN45-AR cells. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3; Student's t-test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001). (E) MGC803-AR and (F) MKN45-AR cells were treated with siRNA targeting DUSP1, siRNA control, or triptolide, respectively, and exposed to Apa for 24 h at different concentrations. Cell viability was determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. The statistical differences between Apa + triptolide and Apa only groups are above the curve; statistical differences between the scramble siRNA NC + Apa and si-DUSP1 + Apa groups are shown to the right of the curve. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=5; Student's t-test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001). (G) MGC803-AR and (H) MKN45-AR cells were transiently transfected with a scramble siRNA or DUSP1 siRNA, then treated with 10 µM Apa or 10 µM Apa + 1 µM triptolide for 5 days. Cells were stained with crystal violet and analyzed. Apa, apatinib; AR, Apa-resistant DUSP, dual-specificity phosphatase-1; si, small interfering RNA; CON, control; NC, negative control.