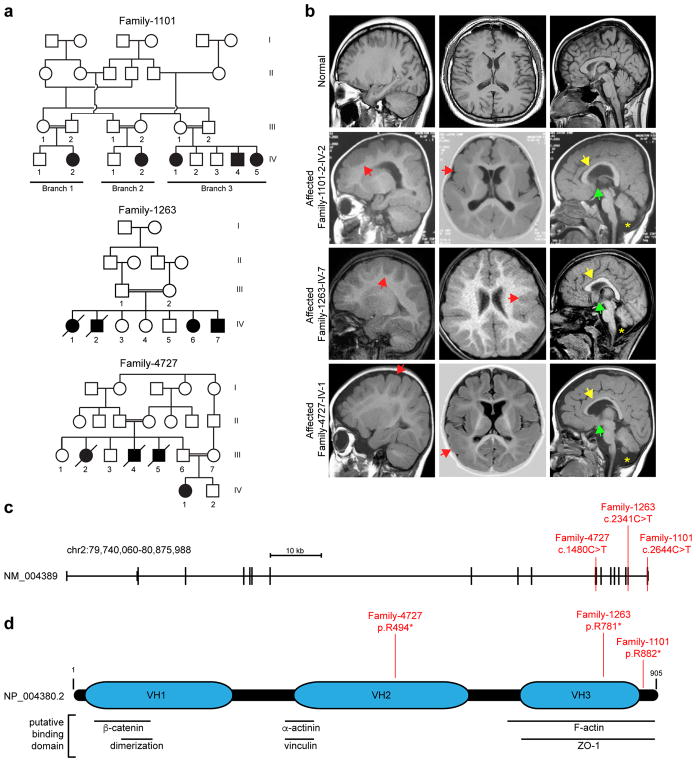
Figure 1. Identification of homozygous truncating CTNNA2 mutations in families with pachygyria.
(a) Pedigrees of three consanguineous families. Parental consanguinity: double bar. Asterisk: sampled individual, Square: male, Circle: female, Filled: affected.
(b) Sagittal, axial, and midline sagittal MRI with symmetrically thickened cortex (red arrowheads) and paucity of cortical gyri, consistent with pachygyria. Patents present with thin corpus callosum (yellow arrowheads), absent anterior commissure (green arrowheads), and fluid cavity as a result of cerebellar hypoplasia (mega cisterna magna, yellow asterisk).
(c) CTNNA2 genomic organization, and location of mutations in Families 1101, 1263 and 4727 in red.
(d) CTNNA2 905 aa polypeptide (Entrez NP_004380.2) with Vinculin Homology domains (VH1-3), and putative protein binding sites. Patient homozygous truncating mutations in red.