Figure 1. Combined effect of radiation and immunotherapy.
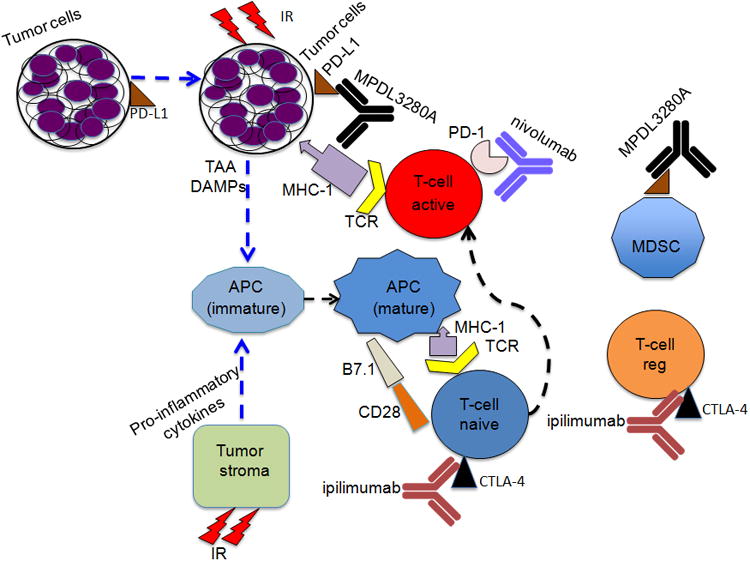
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) are receptors expressed on T-cells and engagement with their ligands (B7-1 or B7-2 and B7-H1 or B7-H2 respectively) restricts T-cell activity. Anti-CTLA-4 antibody and RT in combination induce systemic anti-tumor response in number of carcinomas. PD-1, a cell surface receptor functions as an immune check point and PD-L1 is expressed on a wide variety of cells such as antigen presenting cells, epithelial and endothelial cells. Preclinical studies indicate that combination of RT and Inhibition of PD-1/ or PD-1 ligand increases cytotoxic T cell activity and reduces myeloid-derived suppressor cells. [TCR-T-cell receptor, MHC-1-major histocompatibility complex, APC- Antigen presenting cell, MSDC-myeloid derived suppressor cell, regulatory T-cell (T-cell reg), DAMPs-damage associated molecular patterns (involved in maturation of APCs (dendritic cells), TAA- tumor associated antigens, MPDL3280A- anti-PDL1, Nivolumab –anti-PD1 and ipilimumab- anti-CTL4]. The figure is modified from reference (75).
