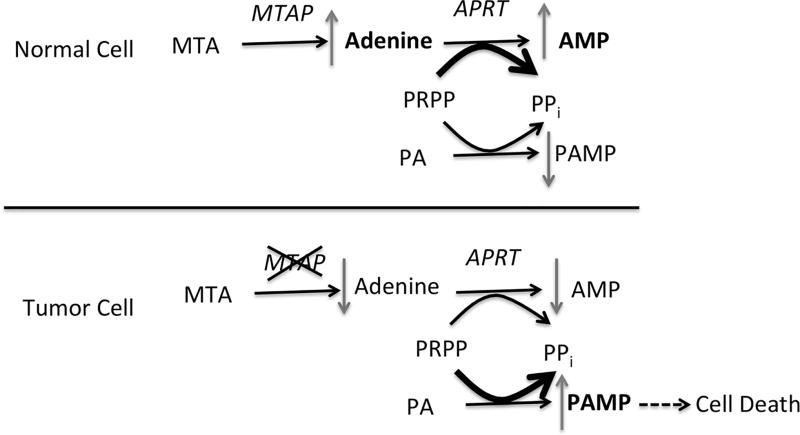
Figure 1.
MTAP protection strategy. In MTAP+ cells MTA is converted to adenine, which is then used to synthesize AMP by the action of APRT, which transfers the ribose and phosphate from PRPP. Purine analogs (PA) must also be converted to nucleosides (PAMP) by the transfer ribose and phosphate from PRPP (although the exact phosphoribosyltransferase used can vary depending on the analog). High concentrations of MTA inhibit the conversion of PA to PAMP by either competition for PRPP, or competition for APRT. In MTAP− cells (bottom), MTA is not converted to adenine, so no competition takes place, resulting in increased production of toxic PAMP.