Figure 4. CDK4/6 inhibition drives NF-κB-mediated upregulation of NGF, BDNF, and HGF.
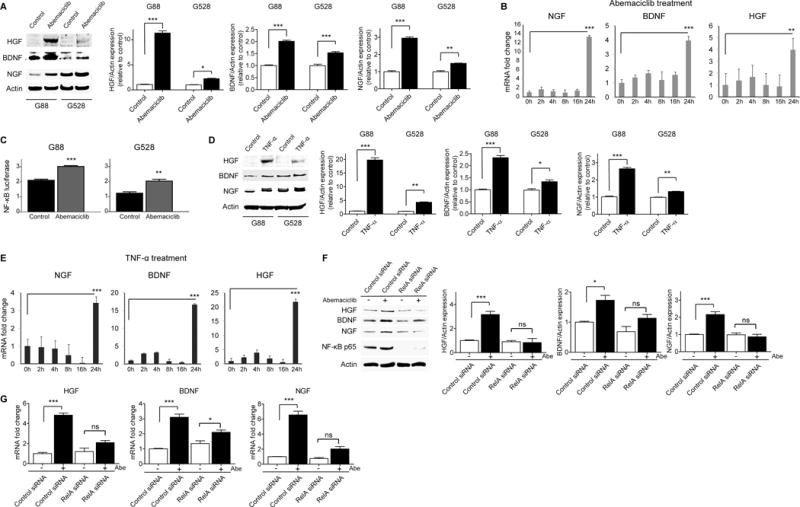
(A–B) Abemaciclib (1.5 μM) treatment upregulates NGF, BDNF, and HGF expression. Shown is an immunoblot using antibodies specific for NGF, BDNF, and HGF. Protein expressions were quantitated and plotted (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001; two-tailed t-test). mRNA levels of NGF, BDNF, and HGF in G88 were detected with qRT-PCR following abemaciclib treatment at different time points (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-tailed t-test). (C) Abemaciclib (1.5 μM) increases NF-κB activity detected with a luciferase reporter assay at 24 hours of treatment (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-tailed t-test). (D–E) TNF-α (10 ng/ml) treatment upregulates NGF, BDNF, and HGF. Shown is an immunoblot using antibodies specific for NGF, BDNF, and HGF. Protein expressions were quantitated and plotted (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001; two-tailed t-test). mRNA levels of NGF, BDNF, and HGF in G88 were detected with qRT-PCR following TNF-α treatment at different time points (***P < 0.001; two-tailed t-test). (F–G) Silencing NF-κB with a specific siRNA reverses the upregulation of NGF, BDNF, and HGF following abemaciclib (1.5 μM) treatment. Shown is an immunoblot using antibodies specific for NGF, BDNF, HGF, and NF-κB p65. Protein expressions were quantitated and plotted (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001; two-tailed t-test). mRNA levels of NGF, BDNF, and HGF were detected with qRT-PCR following 24 hours of abemaciclib (1.5 μM) treatment in the presence of control and RELA siRNA (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001; two-tailed t-test). All values are mean ± SEM and from three biologically independent samples.
