Figure 5.
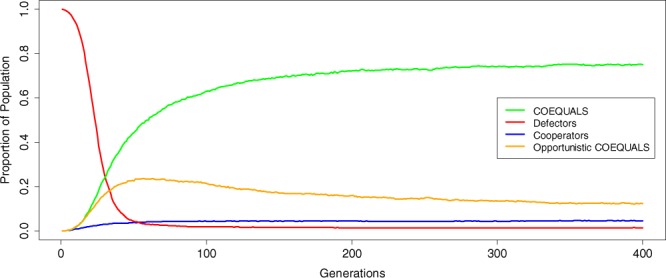
Robustness of COEQUALS to a variant that seeks to defect in the final game of a generation. The figure indicates the limited success of Opportunistic COEQUALS—a strategy that mimics COEQUALS, yet attempts to identify the final one-shot game in a generation and defect in it. Theoretically, COEQUALS appears vulnerable to this variant because it would gain the benefits of free-riding and impose the costs of cooperation on COEQUALS just prior to reproduction, thus acquiring a definitive fitness advantage. However, when the final game of a generation remains unknown, Opportunistic COEQUALS might defect prior to the final round of a generation, thus creating wealth inequality that gives COEQUALS agents the opportunity to avoid adopters of the variant and return to higher levels of fitness via mutually cooperating with other COEQUALS agents. The results in Fig. 4 dovetail with that possibility. The results show the median of the distribution of each strategy’s population share across every generation of the simulation. COEQUALS and the opportunistic variant hold the same median value until the 15th generation of the simulation at which point the median of the distribution containing COEQUALS’ population shares increases relative to that of Opportunistic COEQUALS. Opportunistic COEQUALS, however, remains a non-trivial proportion of the population; the median of its distribution of population shares reaches a maximum value of 0.236 in the 57th generation of the simulation and it remains at 0.123 at the end of the simulation. Despite this presence, the variant is eclipsed by the success of COEQUALS. The median value of COEQUALS’ distribution of population shares reaches its maximum value in the 346th generation and hovers about this value through the end of the simulation, reaching it again in the 398th generation. Indeed, from the 200th generation onward, it continues to increase the median value of the distribution of its population shares, growing from approximately 0.72 at g = 200 to a final value of 0.75 at g = 400. Cooperators and defectors, on the contrary, constitute a trivial portion of the population throughout the simulation runs, with the latter strategy falling precipitously from its initial incumbent state.
