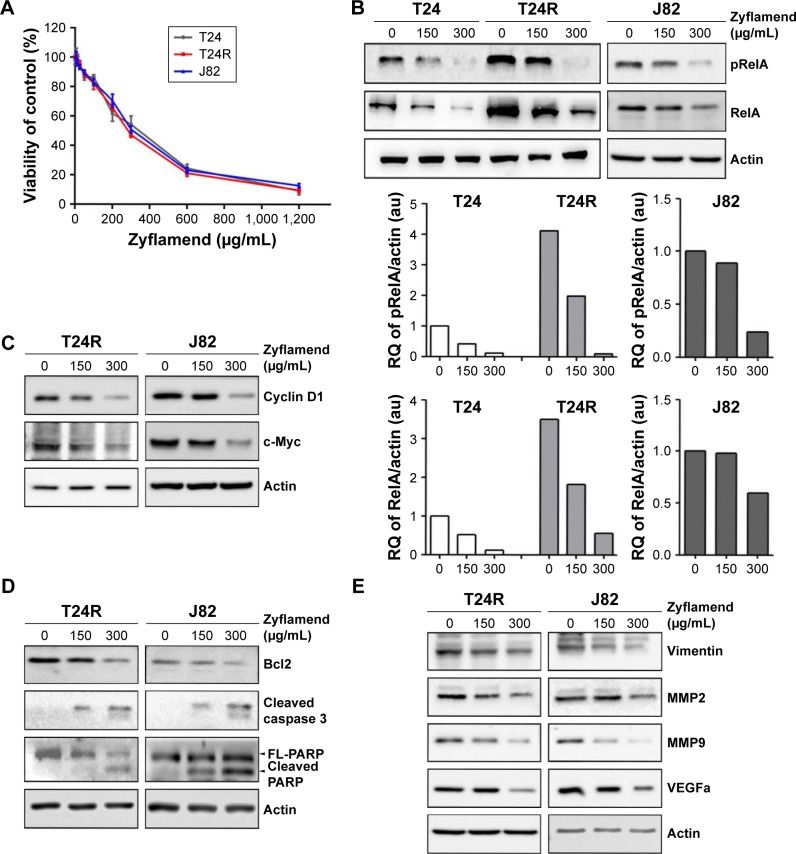
Figure 2.
Zyflamend inhibited cell survival of UBC cells and suppressed NFκB signaling pathway.
Notes: (A) Cell viability of UBC cells treated with Zyflamend at various concentrations (0–1,200 μg/mL) for 72 h detected by MTT assay. Data are presented as mean ± SE. Western blotting analysis on T24, T24R, and J82 cells treated with the indicated concentrations of Zyflamend for the expression levels of NFκB transcriptional factor (B). The graphs depict the quantification data of Western blotting on pRelA and total RelA, which were analyzed by ImageJ software. The NFκB downstream targets related to cell proliferation (C), survival (D), and invasion/angiogenesis (E) were also examined after 48 h treatment with Zyflamend.
Abbreviations: UBC, urinary bladder cancer; NFκB, nuclear factor kappaB; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; SE, standard error; T24R, cisplatin-resistant T24 cell; RQ, relative quantification.